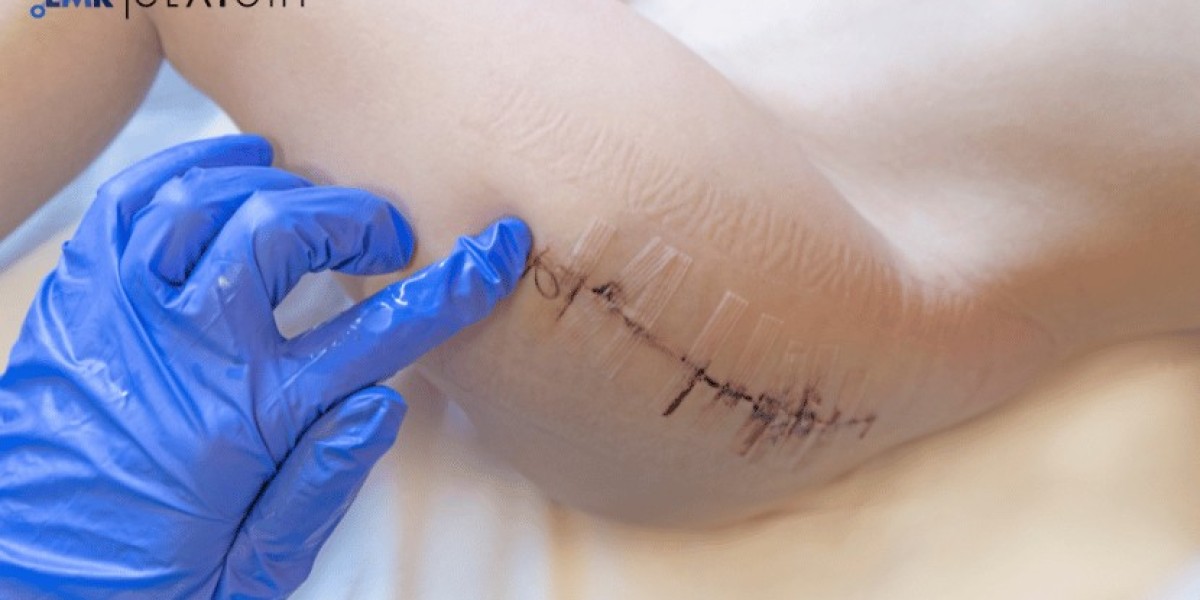
Wound closure strips, also known as adhesive strips or surgical strips, are medical devices designed to close wounds and incisions without the need for sutures or staples. These strips are highly valued in the medical field for their ease of application, reduced scarring, and lower risk of infection. Setting up a wound closure strip manufacturing plant involves careful planning, advanced production techniques, and strict adherence to medical standards. This article provides a detailed guide on the processes, equipment, and key considerations for establishing a successful wound closure strip manufacturing facility.
Understanding Wound Closure Strips
Wound closure strips are adhesive-based medical products used to secure the edges of wounds or surgical incisions. Made from hypoallergenic materials, these strips are gentle on the skin while providing strong adhesive properties to ensure effective wound closure. Their non-invasive nature makes them a preferred choice for minor surgical procedures and first-aid applications.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/wound-closure-strip-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Key Processes in Wound Closure Strip Manufacturing
- Raw Material Procurement
- High-quality materials such as medical-grade adhesives, backing materials (like non-woven fabric or polyurethane), and release liners are sourced.
- Adhesive Coating
- The adhesive is uniformly applied to the backing material using specialised coating machines, ensuring consistent thickness and adherence properties.
- Lamination
- The coated backing material is laminated with a release liner to protect the adhesive until use.
- Cutting and Shaping
- The laminated material is cut into strips of standard sizes using precision cutting machines.
- Sterilisation
- The wound closure strips are sterilised to eliminate any contaminants, ensuring they are safe for medical use.
- Packaging
- The strips are individually packaged in sterile pouches or boxes, clearly labelled with usage instructions and product details.
Essential Equipment for a Wound Closure Strip Manufacturing Plant
Setting up a wound closure strip manufacturing plant requires specific machinery to ensure efficiency and product quality. Key equipment includes:
- Adhesive Coating Machines: For applying medical-grade adhesive to backing materials.
- Laminating Units: To bond the adhesive-coated material with a protective release liner.
- Precision Cutting Machines: For creating uniform strips of standard sizes.
- Sterilisation Equipment: Such as ethylene oxide or gamma radiation systems to sterilise the finished products.
- Packaging Machines: For sealing strips in sterile pouches or boxes.
- Quality Testing Instruments: To ensure the adhesive strength, material durability, and sterility of the products.
Designing the Plant Layout
An efficient plant layout ensures smooth operations and compliance with medical manufacturing standards. Key considerations include:
- Raw Material Storage: Dedicated areas for storing adhesive, backing materials, and release liners under controlled conditions.
- Production Line: A streamlined workflow for coating, laminating, cutting, and packaging processes.
- Quality Control Lab: Equipped to test adhesive properties, sterility, and product durability.
- Sterilisation Unit: A secure area for sterilising the finished products.
- Packaging and Storage: Space for packaging the strips and storing them before distribution.
- Waste Management System: For handling and disposing of production waste in compliance with environmental regulations.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
Maintaining consistent quality is crucial for wound closure strips, given their medical applications. Key quality control practices include:
- Raw Material Testing: Verifying the adhesive strength and compatibility of backing materials.
- Process Monitoring: Ensuring uniformity in adhesive application and lamination.
- Product Testing: Checking for sterility, adhesive performance, and durability of the strips.
- Hygiene Standards: Implementing strict cleanliness protocols to prevent contamination during production.
Regulatory and Licensing Requirements
Setting up a wound closure strip manufacturing plant involves compliance with stringent medical regulations. Key requirements include:
- Medical Device Certification: Ensuring the product meets international standards for medical devices.
- Sterility Compliance: Adhering to protocols for sterilisation and packaging.
- Labelling Regulations: Providing clear and accurate product information on packaging.
- Environmental Clearances: Implementing waste management systems in line with regulatory requirements.
- Workplace Safety Standards: Ensuring the safety of workers and equipment during production.
Applications of Wound Closure Strips
Wound closure strips are widely used across various medical and non-medical applications, including:
- Surgical Procedures: To close minor incisions and reduce the need for sutures or staples.
- First Aid: For closing small cuts and lacerations in emergency situations.
- Paediatrics: As a gentle alternative for wound closure in children.
- Cosmetic Surgery: To minimise scarring and enhance the healing process.
- Home Care: For post-surgical care and minor wound management.
Sustainability in Manufacturing
Sustainability is increasingly important in medical manufacturing. Key practices include:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Using biodegradable or recyclable materials for backing and packaging.
- Energy Efficiency: Adopting energy-saving technologies in production processes.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing recycling initiatives for scrap materials and by-products.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Partnering with suppliers who follow environmentally responsible practices.
Market Trends and Opportunities
The wound closure strip market is growing due to rising awareness of non-invasive medical solutions and advancements in healthcare technology. Key trends include:
- Increased Adoption in Healthcare: Surgeons and healthcare providers increasingly prefer wound closure strips for their ease of use and reduced risk of infection.
- Demand for Customisation: Growth in demand for strips tailored for specific medical applications, such as paediatrics or cosmetic surgery.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Developing regions are adopting advanced wound care products, boosting market growth.
- E-Commerce Opportunities: Online platforms provide a direct-to-consumer sales channel for wound closure products.
Challenges in the industry include:
- Raw Material Costs: Managing the fluctuating prices of adhesives and backing materials.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Adhering to stringent medical device regulations.
- Competition: Standing out in a competitive market with established players.
By focusing on quality, innovation, and sustainability, manufacturers can establish a successful wound closure strip production facility and meet the growing demand for advanced wound care solutions.