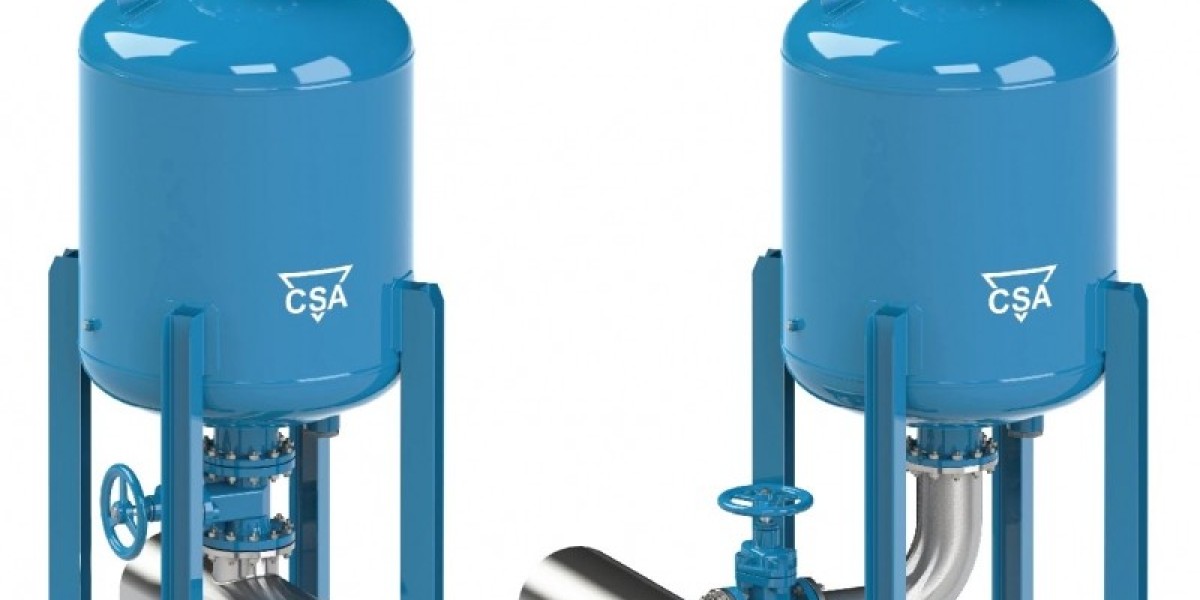
The surge tank market, while experiencing steady growth across various industries such as hydropower, oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing, faces several restraints that may hinder its full potential. Surge tanks are critical components in managing pressure fluctuations in pipelines and ensuring the integrity of hydraulic systems. However, challenges such as high initial costs, lack of awareness, technological limitations, and regulatory complexities present barriers to the widespread adoption of surge tank solutions. This article discusses the key restraints facing the surge tank market, the challenges these pose, and potential solutions to overcome them.
1. High Initial Investment Costs
One of the most significant restraints in the surge tank market is the high upfront cost associated with the purchase and installation of surge tanks. Surge tanks, especially those designed for large-scale applications in industries like oil and gas or hydropower, can be expensive due to the materials, technology, and engineering expertise required. The cost of installation, including site preparation, welding, and integration with existing infrastructure, further adds to the financial burden.
For smaller companies, particularly those in developing regions, these high costs can be prohibitive. This creates a challenge for the widespread adoption of surge tanks, particularly in industries where budget constraints are a concern. To overcome this restraint, surge tank manufacturers must focus on developing more cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality or safety.
2. Limited Awareness and Understanding
In many industries, the concept of surge tanks and their role in pressure management systems is not widely understood. Despite their critical importance in maintaining the safety and efficiency of pipelines, surge tanks are often perceived as an afterthought or optional component. Lack of awareness about the potential consequences of pressure fluctuations, such as pipe ruptures, equipment damage, and safety risks, leads some companies to overlook surge tanks in their infrastructure planning.
Moreover, in emerging markets, where industrialization is rapidly increasing, there may be insufficient technical knowledge about surge tank systems and their benefits. This lack of awareness can delay or inhibit the adoption of surge tank solutions. To address this restraint, surge tank manufacturers and industry stakeholders must invest in educational efforts and promote the importance of surge tanks through marketing, training, and partnerships with local authorities.
3. Technological Limitations
While surge tank technology has evolved over the years, there are still certain limitations that restrict its effectiveness and applicability in some industries. Traditional surge tanks, although functional, are often limited in terms of their ability to monitor real-time pressure data, predict future pressure surges, and integrate with broader digital infrastructure.
With the increasing demand for smart, automated solutions in industrial sectors, surge tanks that lack modern features like IoT sensors, predictive analytics, and remote monitoring systems may be seen as outdated by operators seeking greater control and efficiency. The absence of digital capabilities can make surge tank systems less attractive, especially in industries looking for advanced solutions to optimize operations.
To address this challenge, surge tank manufacturers must focus on integrating digital technologies into their products to enhance their capabilities. Smart surge tanks equipped with real-time monitoring and data analysis tools can offer more precise and predictive solutions, making them more appealing to a tech-savvy market.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The surge tank market is also impacted by varying regulatory requirements across different regions and industries. Different countries or local jurisdictions may have different standards for the design, installation, and maintenance of surge tanks. Compliance with these regulations requires manufacturers to tailor their surge tank products to meet specific local standards, which can increase costs and complexity.
Moreover, frequent changes in safety and environmental regulations can cause uncertainty for companies looking to invest in surge tanks. The need for constant updates to meet new compliance standards can create additional challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike.
While surge tanks are crucial for ensuring pipeline safety and operational stability, the complexity of navigating diverse regulatory landscapes can slow down market growth. To mitigate this restraint, surge tank manufacturers must stay updated with regulatory changes and work closely with local authorities to ensure compliance. Simplifying compliance processes through standardized global regulations could also help accelerate market development.
5. Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Although surge tanks are designed to improve pipeline safety and reduce pressure fluctuations, they still require regular maintenance and inspections to function effectively. Over time, surge tanks can experience wear and tear, corrosion, or sediment accumulation, especially in industries like oil and gas where the materials being transported can be corrosive.
Additionally, surge tanks must be periodically calibrated to ensure that they are functioning as intended. The complexity of maintenance can be a deterrent for some companies, especially those with limited in-house expertise or resources for managing these systems.
To overcome this challenge, manufacturers can design surge tanks that require less frequent maintenance and are more resilient to environmental stressors. Advanced materials, corrosion-resistant coatings, and simplified maintenance procedures could reduce the operational burden on companies and increase the appeal of surge tank systems.
6. Space Constraints and Installation Issues
Surge tanks, particularly large-scale models used in hydropower plants or oil and gas pipelines, require significant space for installation. In urban or densely populated areas, finding suitable locations for surge tanks can be a challenge, as space may be limited or expensive. Additionally, the installation process itself may be complex, requiring modifications to existing infrastructure, extensive engineering work, and downtime during construction.
This can be a significant barrier in areas where land is scarce, or projects need to be completed quickly. To address these challenges, manufacturers may need to develop more compact, modular surge tank designs that are easier to install in constrained spaces.
Conclusion
While the surge tank market holds significant growth potential across various industries, it faces several restraints that may hinder its development. High upfront costs, limited awareness, technological limitations, regulatory complexities, maintenance challenges, and space constraints are all factors that can slow down market adoption. By addressing these issues through technological innovation, cost-effective solutions, educational efforts, and strategic collaborations, manufacturers can overcome these barriers and unlock new opportunities for surge tank systems in industries worldwide.