In today's digital world, the way we share and access information has evolved significantly. One of the most interesting developments is the rise of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networks. This blog will explain what P2P networks are, how they work, their advantages, and some common uses in simple terms. So, let’s now start the blog.
What is a Peer-to-Peer Network?
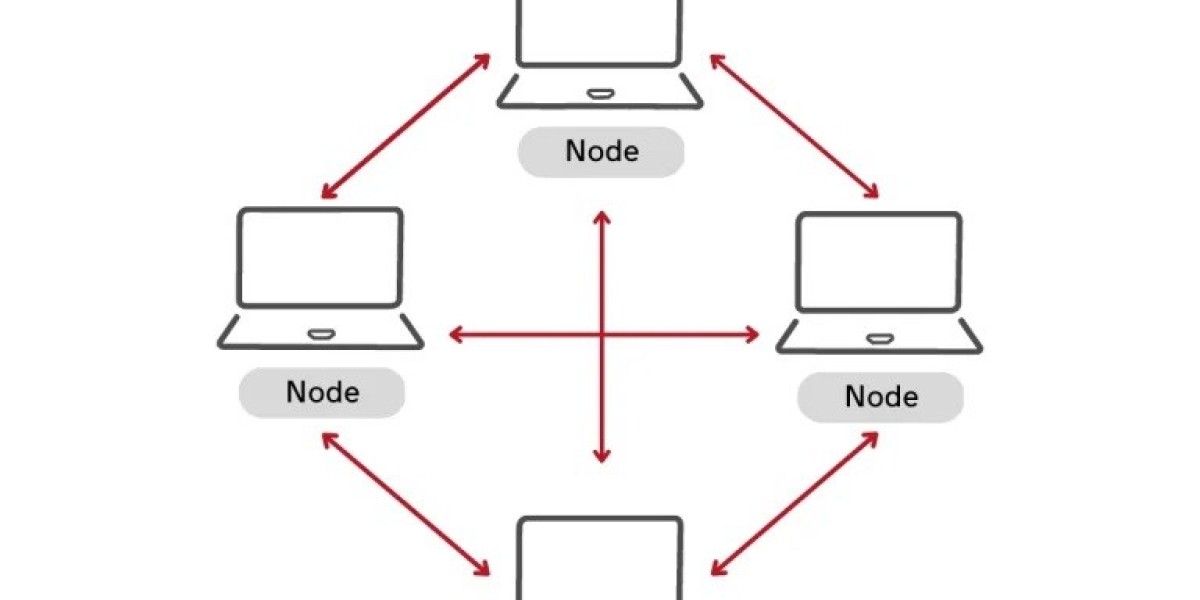
A Peer-to-Peer network is a type of network where computers (or "peers") connect directly with each other to share resources, files, or information. Unlike traditional client-server models, where one central server provides data to many clients, in a P2P network every participant can act as both a client and a server. This means that each computer can send and receive data, making the network decentralized and more flexible.
How Do P2P Networks Work?
In a P2P network, when one user wants to share a file, they upload it to their computer. Other users on the network can then connect to that computer to download the file. This direct connection between users eliminates the need for a central server.
Key Components of P2P Networks:
- Peers: These are the individual computers or devices connected to the network. Each peer can share and access resources without relying on a central server.
- Protocols: P2P networks use specific rules or protocols that define how data is shared and transmitted. Common protocols include BitTorrent for file sharing and the Gnutella protocol for search functions.
- Distribution: When a user downloads a file, they often download pieces from multiple peers simultaneously. This distribution speeds up the download process and reduces the load on any single peer.
Advantages of P2P Networks
P2P networks offer several benefits that make them appealing for various applications:
- Decentralization
Since P2P networks do not rely on a central server, they are less vulnerable to failures or attacks. If one peer goes offline, others can still share and access files.
- Scalability
P2P networks can easily grow. As more users join the network, they add more resources. This makes it easy to accommodate increasing demand without needing additional infrastructure.
- Cost-Effective
Running a P2P network can be less expensive than maintaining a server-based system. Users share resources, reducing the need for costly servers and bandwidth.
- Faster File Sharing
Because files are shared across multiple peers, download speeds can be faster. Users can download pieces of a file from different sources simultaneously, leading to quicker access.
Common Uses of P2P Networks
P2P networks have various applications, ranging from file sharing to blockchain technology. Here are some of the most common uses:
- File Sharing
One of the most popular uses of P2P networks is file sharing. Applications like BitTorrent allow users to share large files, such as movies, music, and software, efficiently. This method has gained popularity due to its speed and ease of use.
- Streaming Services
Some streaming services use P2P technology to distribute content. For example, platforms like Popcorn Time allow users to stream movies and shows by sharing data directly with each other, reducing the need for expensive servers.
- Online Gaming
Many online games use P2P connections to allow players to connect and interact directly. This setup can enhance gameplay and reduce latency, providing a smoother experience for players.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
P2P networks are fundamental to blockchain technology. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin rely on decentralized networks to manage transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. Each participant (or node) in the network has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
- Collaboration Tools
Some collaboration tools utilize P2P technology for sharing documents and data among users. This allows team members to collaborate more efficiently without relying on a central server.
Challenges of P2P Networks
While P2P networks have many advantages, they also face some challenges:
- Security Risks
Since users share files directly, there is a risk of downloading malicious software. Users must be cautious about what they download and from whom.
- Legal Issues
P2P networks have been associated with copyright infringement, particularly in file-sharing applications. Users need to be aware of the legal implications of sharing certain content.
- Network Management
Managing a P2P network can be more complex than a traditional server-based network. Issues like data consistency and user reliability can arise.
Conclusion
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks have transformed the way we share and access information in the digital age. With their decentralized structure, they offer numerous advantages, including faster file sharing, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. From file-sharing applications to blockchain technology, P2P networks play a crucial role in various industries.
However, users must also be aware of the challenges associated with P2P networks, such as security risks and legal issues. As technology continues to evolve, P2P networks will likely remain a significant part of our online experience, shaping how we interact with each other and access information.