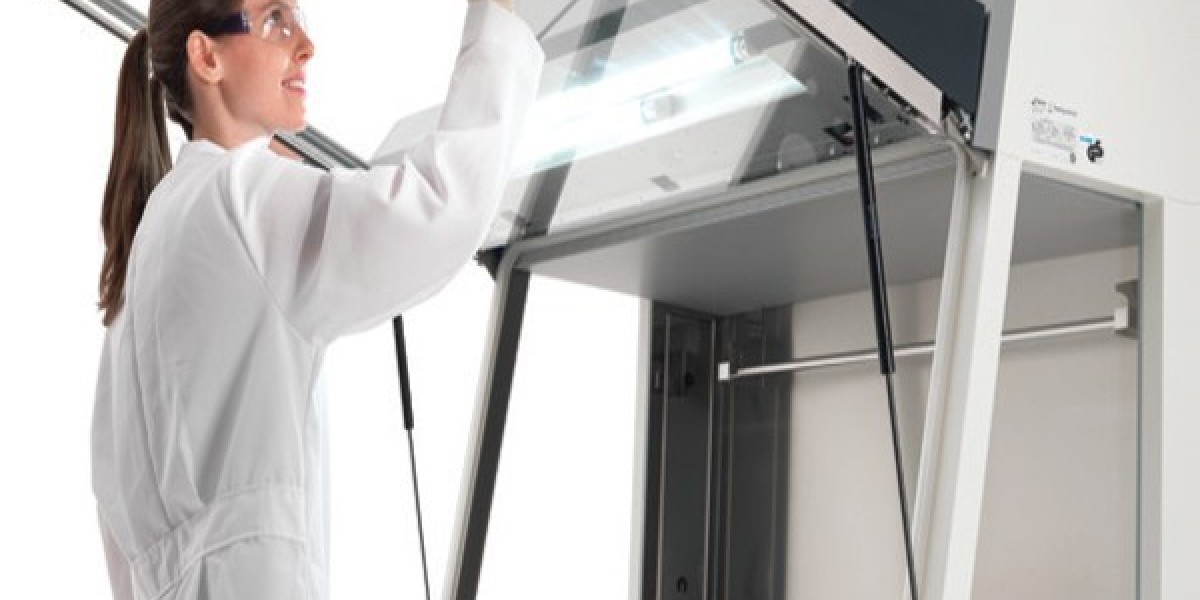
Biological safety cabinets, also known as biosafety cabinets or BSCs, are essential equipment used in laboratories to protect workers and the environment from exposure to hazardous biological materials like bacteria, viruses, rickettsiae or potentially infectious substances. They provide an important physical barrier that contains and controls potential contamination or exposure during handling and manipulation of biological materials. In this article, we will explore the key components, classifications and functions of biological safety cabinets.
Types of Biological Safety Cabinets
There are three main classes of biological safety cabinets categorized based on their filtration and airflow design features:
Class I: These are ventilated cabinets that provide personnel and environmental protection through unidirectional inward airflow and high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration of exhausted air. Exposure is controlled through inward velocity capture of aerosols generated in the cabinet work area. Class I cabinets are primarily used for low-risk procedures.
Class II: Class II cabinets have a higher level of protection than Class I and provide both personnel and environmental protection through unidirectional inward airflow and HEPA-filtered laminar flow. They have an open front with inward airflow and come in two types - Class II, Type A1 and Class II, Type A2 depending on whether they exhaust air back into the laboratory (A1) or vent it to the outside (A2). These are suitable for low to moderate risk activities.
Class III: Class III cabins offer the highest level of protection and are totally enclosed, gas-tight cabinets with a non-opening front window and gloves built into the cabinet's internal work access ports. They maintain negative pressure inside the Biological Safety Cabinets and provide the greatest level of containment through a double-HEPA filtered recirculated airflow system, giving 360-degree product and personnel protection. Class III BSCs are designed for handling risky infectious aerosols and are ideal for advanced pathology and microbiology laboratories.
Key Components of a Biological Safety Cabinet
Regardless of class, all biological safety cabinets have certain key common components that enable their effective functioning:
- Work access ports/viewing window: This is a front opening that allows manipulations and work inside the cabinet protected space. Class III units come with built-in arms/gloves.
- Blower/fan unit: This comprises the high-volume centrifugal fans that power the inward unidirectional airflow system.
- Pre-filters: These washable pre-filters capture large particulates and reduce contamination of the main HEPA filters.
- HEPA/ULPA filters: High-efficiency particulate arresting (HEPA) or ultra-low particulate air (ULPA) filters remove 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns or larger from the airstream.
- Ultraviolet light: An internal UV light installed in the airflow exhaust duct sterilizes microorganisms, preventing their discharge outside the cabinet.
- Airflow monitoring: Pressure gauges and sensors ensure proper airflow velocities are maintained for safety. Alarms indicate filter failures or pressure drops.
- Error alarms: Audible/visual alarms alert users of deviations like filter ruptures that compromise protection levels.
Functions of Biological Safety Cabinets
Some key functions provided by biologic safety cabinets include:
- Containment: Containing hazardous aerosols and droplets generated during microbiological procedures within the filtered cabinet area to prevent exposure.
- Filtration: HEPA/ULPA filters remove and contain hazardous particulates from the airstream before exhaust/recirculation.
- Personnel protection: Unidirectional laminar inward airflow and physical barrier protect the user from exposure to hazardous biological materials being handled.
- Product protection: The controlled sterile environment protects cell cultures and other sensitive materials from external contaminants during procedures.
- Decontamination: UVGI lights in cabinets sterilize microbes in the exhaust airstream before release to the outside environment.
- Safe sample transfer: The cabinets allow transferring of infected materials between primary and secondary containers at low biohazard risk.
- Energy efficiency: Class II BSCs recirculate 70-90% of HEPA-filtered air within the cabinet, conserving conditioned room air usage.
Ensuring Proper Use and Maintenance of Biologic Safety Cabinets
For biologic safety cabinets to provide optimal protection levels over their service lifetimes, users must follow proper operating procedures and facilities should implement regular maintenance and certification programs. Key points include:
- Training staff on correct equipment usage to avoid compromising inward airflow.
- Scheduling annual certification to NSF49 standards involving airflow velocity tests and HEPA filter leak checks.
- Conducting routine filter replacements as per usage guidelines.
- Monitoring for pressurization failures or deviations via audible/visual alarms.
- Implementing regular disinfection protocols to prevent cross-contamination buildup.
- Adhering to authorized procedures for transporting materials in and out of the cabinet area.
Get more insights on Biological Safety Cabinets
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement.
(LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)