Introduction
The Role of AI in Modern Cybersecurity
Not only are opportunities rising as we seek technological advancement encompassing AI in cybersecurity, but also threats are augmenting. As the varieties of threats in cyberspace continue to manifest themselves, the future of AI in cybersecurity holds the key as a critical component that processes large data sets and can detect the molds and patterns of emerging attack fronts.
Overview of the Article
This article provides the reader with information on AI cybersecurity trends, how AI is being utilized and will be utilized in the near and distant future for cybersecurity, associated technologies, the decision-making process regarding the use of AI in cybersecurity, and future trends.
We will discuss the role software development companies can play and their AI use cases for both threat detection and for managing incident response, in addition to the current opportunities and threats that define the landscape of cybersecurity.
Understanding AI in Cybersecurity
Definition of AI and Machine Learning
Emerging AI cybersecurity technologies are the imitation of the human intelligence process using machines. Machine learning cybersecurity capabilities in AI fortify cybersecurity as they infuse artificial intelligence into a system to learn from experience with little coding.
How AI is Used in Cybersecurity
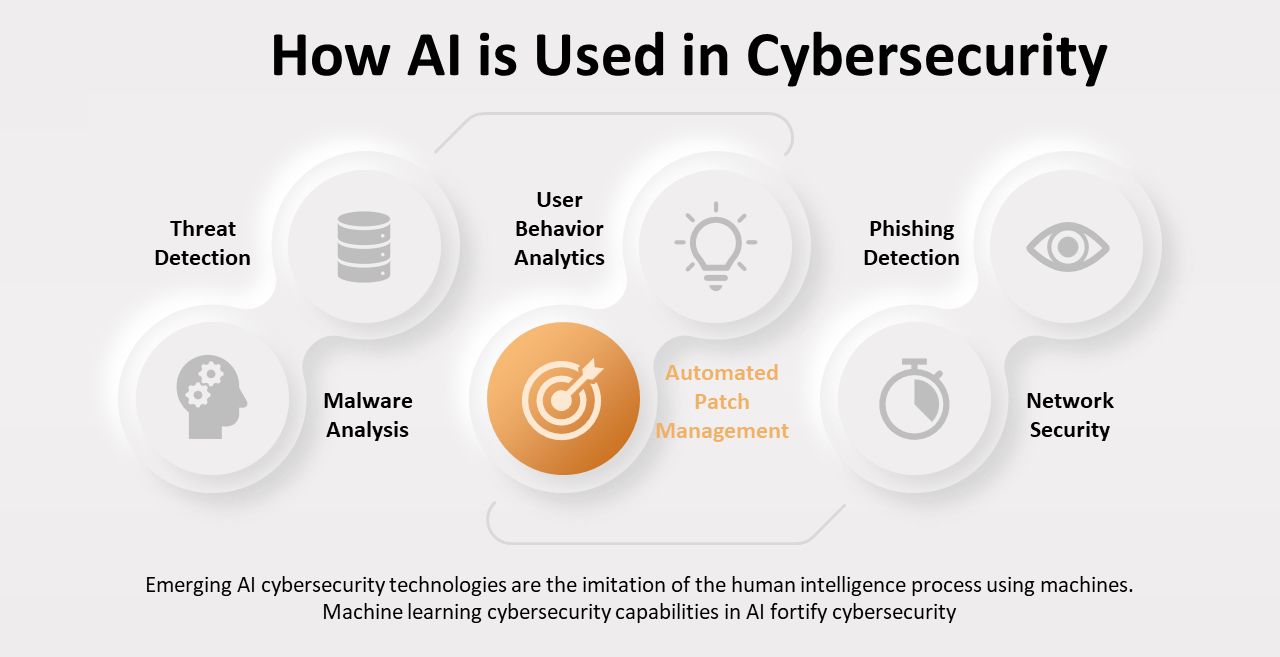
Threat Detection:
AI for threat prevention uses real-time traffic analysis to detect potential security threats based on flow and logs, increasing the system’s detection speed and accuracy.
Malware Analysis:
AI security solutions that work on the basis of samples and logs can also classify and analyze malware, enabling the detection of new diverse strains similar to the previous kind of attack.
User Behavior Analytics:
AI for threat prevention watches user activities to capture patterns that can be compared to those indicating an intrusion.
Automated Patch Management:
Security patching of AI security solutions focuses on prioritizing the application of patches that the intelligence of threats and weaknesses of the systems has determined.
Phishing Detection:
Machine learning methods analyze the content and information in emails received to detect complex phishing scams.
Network Security:
Machine learning approaches are used in firewalls, meaning that a firewall can learn new threats and modify its rules according to those threats.
Emerging AI Technologies in Cybersecurity
AI for threat prevention is still growing, and software development companies are employing advanced AI security packages to combat coverage.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP strengthens threat intelligence as it processes data in forms that might be difficult to use in conventional analysis. This includes its ability to identify the more complicated forms of phishing because it can take into account the context and intentions of emails.
Deepemailsing
Through deep learning in AI security solutions, these algorithms become capable of identifying intricate cyber threats from large amounts of data. They can detect specific patterns and discrepancies that may not be detected by rule-based systems and improve threat detection.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning gives AI models the ability to learn on their own without external help when the threat environment changes. Since such systems receive feedback on successful or unsuccessful actions, software development companies refine their skills in identifying new types of cyber threats.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Several papers and studies show how GANs generate synthetic data that assists AI models in learning patterns and types of anomalies they have not encountered before. Generative adversarial networks in cybersecurity ensure that cybersecurity systems practice how they deal with different types of cyberattacks.
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Prevention
A concept known as AI-driven continuous monitoring and threat-hunting is a strong AI cybersecurity strategy that significantly helps to avoid data breaches and cyberattacks.
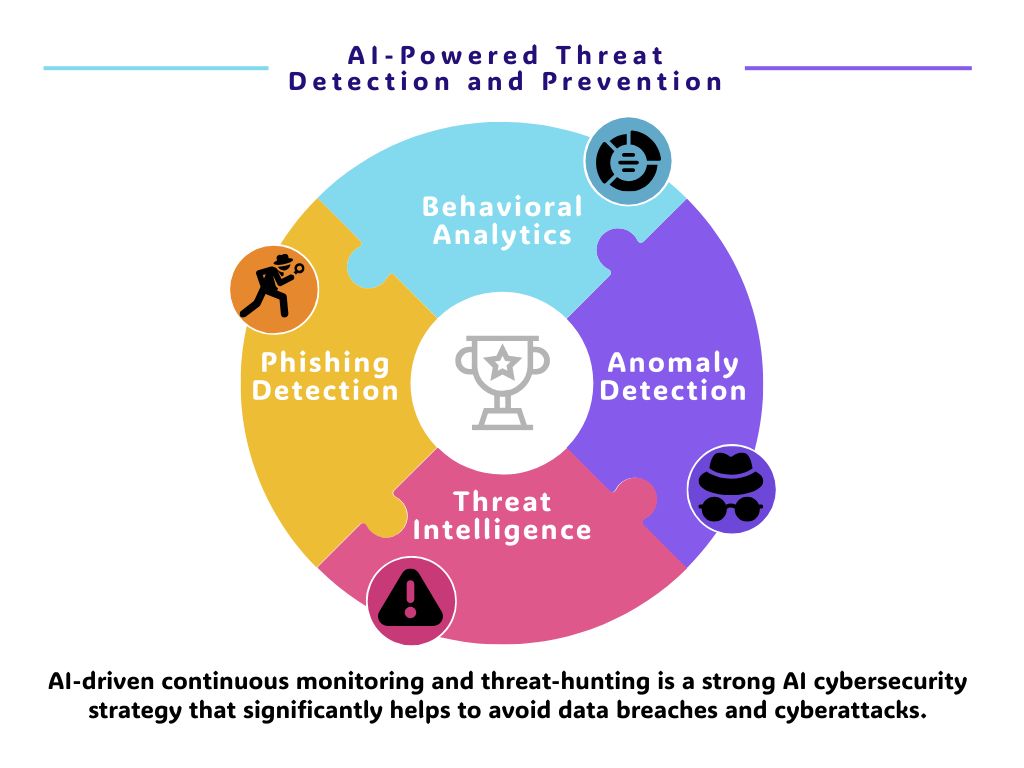
Behavioral Analytics
Artificial intelligence in security can then examine the different patterns of users’ behavior to determine normal and abnormal activities. It allows for the identification of insider threat situations, compromised accounts, and other security incidents based on deviations from the norm.
Anomaly Detection
Machine learning cybersecurity models analyze a large volume of network traffic and system log data to detect anomalies. This capability is effective in identifying novel threats, as signature-based systems may fail to spot them, including zero-day exploits.
Threat Intelligence
AI supports threat intelligence as it combines data into a single source and then analyzes it. Artificial intelligence in security can even forecast potential threats on the horizon, reveal weaknesses, and offer recommendations to help security personnel stay ahead of threats.
Phishing Detection
Machine learning cybersecurity algorithms scan the content of an email, the email details, and the context to identify complex phishing schemes. They learn new forms of phishing methods, and their overall accuracy rate increases with time.
AI-Driven Incident Response
AI-driven continuous monitoring and threat hunting are key functions of emerging AI cybersecurity technologies. These technologies are revolutionizing incident response, making reactions to security breaches much more effective and faster.
Automated Incident Response
An AI system can also perform many administrative measures that require a quick reaction to an incident, such as isolating the compromised systems or blocking the IP used by the threat actor. Automated incident response using artificial intelligence saves time and allows security teams to work on higher-impact aspects of incident management.
Incident Forensics
AI in cybersecurity helps speed up incident forensics by analyzing a vast amount of log data and system artifacts. Machine learning techniques show patterns or interactions that contribute to the goal of identifying the origin and characteristics of security breaches.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Hunting
AI in cybersecurity enables systematic and continuous monitoring of different networks and IT systems with a view of hunting down cyber threats and other related crimes at all times. Advanced AI algorithms can be used to go beyond passive scanning for threats and actively search for threats.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges in AI Cybersecurity
Integrating AI in cybersecurity processes and decisions requires understanding and addressing the possible ethical considerations of AI algorithms in cybersecurity.
Bias in AI Algorithms
AI algorithms may contain factors that have been included intentionally or extracted from the training data used or from the design decisions made. AI for threat prevention could result in affirmative or negative results when it comes to threat detection, hence threatening security or unfairly profiling some users.
Explainability and Transparency
One of the concerns that AI presents to cybersecurity is that some of the algorithms are ‘black boxes,’ and it becomes hard to understand the reasoning that led to some conclusions. It is crucial to create explainable AI models that will help security personnel believe in ethical considerations of AI algorithms in cybersecurity and provide an opportunity to monitor its work.
User Privacy Risks
As AI security solutions track and monitor the vast pool of data, concerns regarding data security are raised. The problem of achieving threat detection with maximum efficiency and maintaining privacy at the same time is rather tricky and implies the usage of adequate data protection tools.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
Continued development in artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is expected to create new products and techniques to counter growing complex threats such as SOCs and endpoint security.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
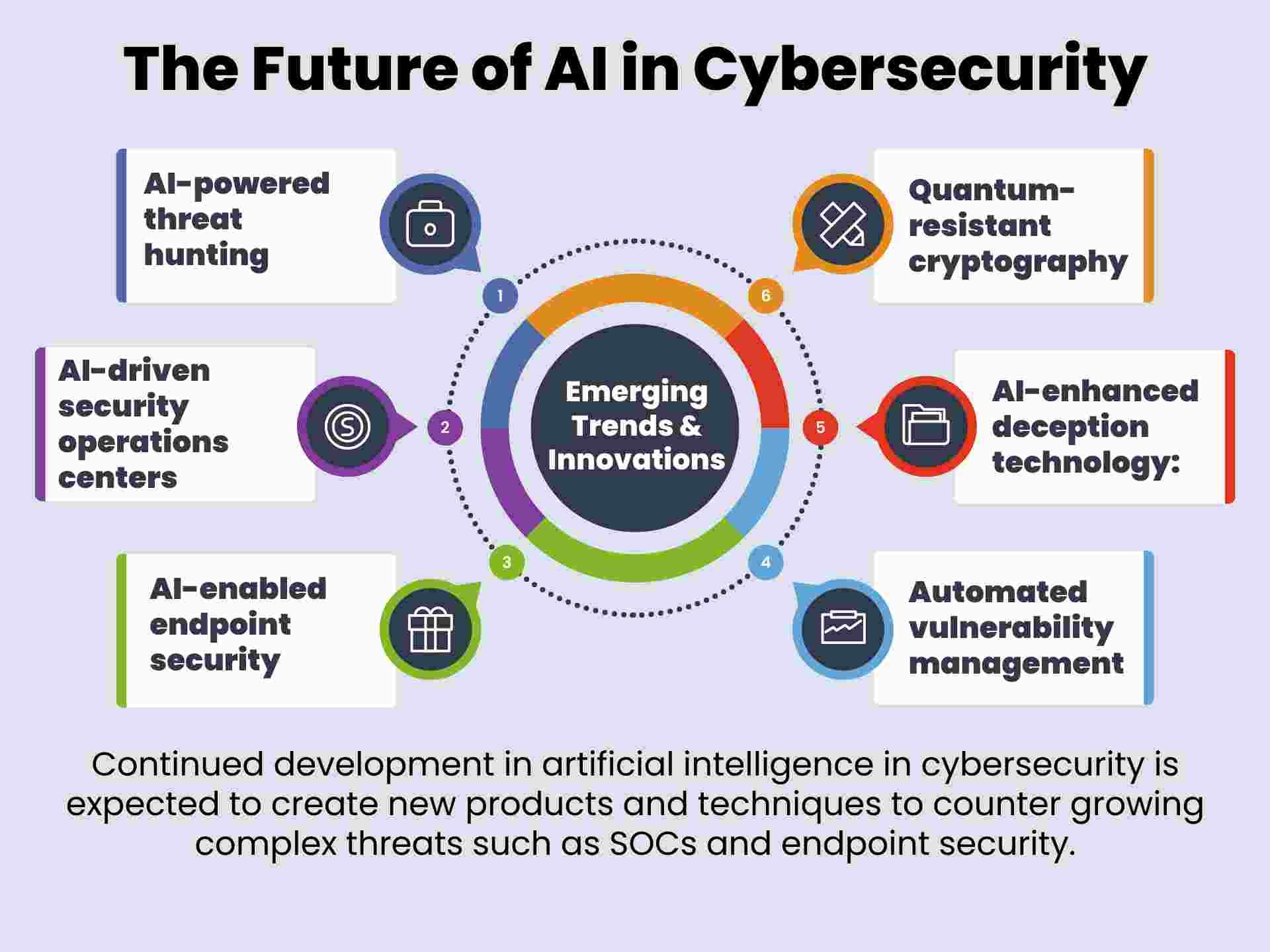
AI-powered threat hunting:
It looks for threats that may be masked or that are yet unknown. Comparing patterns of activity on the networks to find new forms of attack can be easy for emerging AI cybersecurity technologies.
AI-driven security operations centers:
Future trends in AI-enabled security operations centers will improve SOC performance by automating repetitive job duties, setting up priority levels for alerts, and enriching context. As a result, SOCs can respond to security incidents quicker and more effectively.
AI-enabled endpoint security:
An endpoint implements machine learning models that work in real mode to fight cyber threats or attacks and does not require match updates as used in traditional security methods.
AI-enhanced deception technology:
Fresh AI designs and develops complex honeypots and decoy systems to tempt and capture the actions of attackers through innovative AI security solutions.
Automated vulnerability management:
There is also vulnerability scanning along with prioritization of the required patching and the creation of new patches in case of critical manifestations of new vulnerabilities that were not detected earlier.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
Adversarial AI:
Cyber criminals can build their AI structures into criminal activities, and thus, protective AI structures have to enhance and develop their capacities continually.
Skills gap:
Another con that results from a lack of expertise by professionals in the AI fields is difficulties in implementing AI security and managing the integration of sophisticated AI security solutions.
Regulatory compliance:
The emerging new rules of the regulatory environment and shifts in limitations on the use of AI and data protection could be the issues for applying emerging AI cybersecurity technologies.
Opportunities:
Predictive security:
Another advantage of AI for cybersecurity is the possibility of analyzing different kinds of patterns and using the predictions to prevent cyber attacks before they occur.
Autonomous security systems:
The future of AI in cybersecurity, which can identify, combat, and eradicate an attack without much human interaction, is beneficial.
Personalized security:
AI allows for the creation of authoritarian security policies for a particular user or organization, enhancing their security status.
Source: https://www.sigmasolve.com/the-future-of-ai-in-cybersecurity-emerging-technologies-and-trends/


