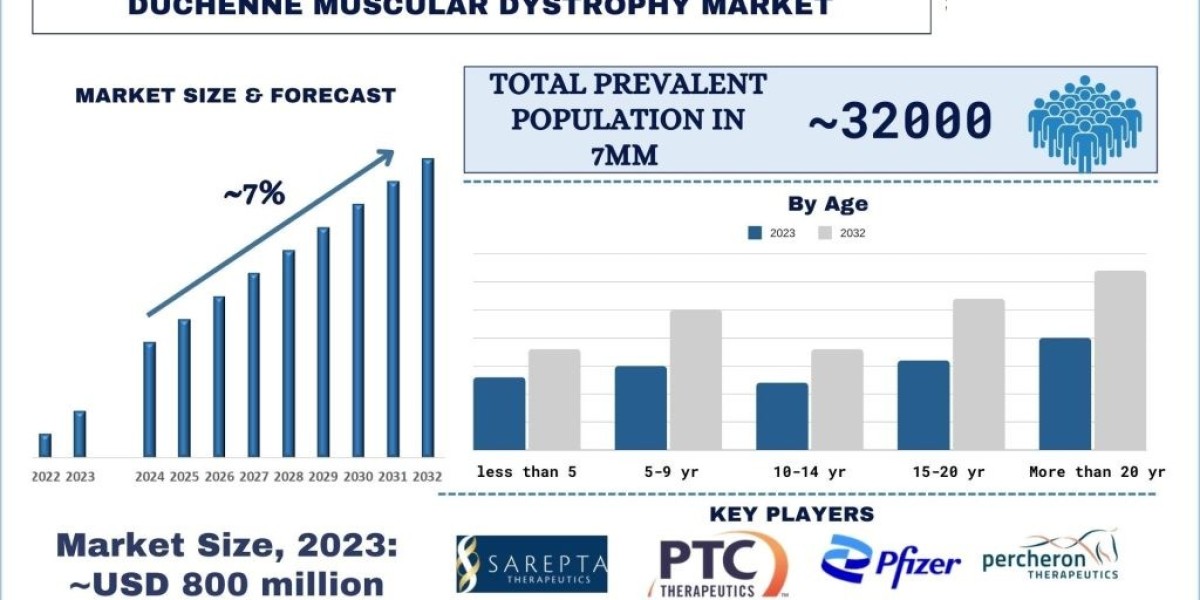
According to the UnivDatos Market Insights analysis, advancements in genetic research, growing awareness campaigns, and advocacy efforts, regulatory agencies and pharmaceutical companies increasingly prioritize patient input in the drug development process, which will drive the 7MM scenario of the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Market. As per their “Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Market” report, the 7MM market was valued at USD 800 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of about ~7% during the forecast period from 2024 – 2032.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is one of the most severe forms of muscular dystrophy, characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. Affecting primarily young boys, DMD leads to significant physical disability and reduced life expectancy. However, recent advancements in medical research have sparked hope, with emerging therapies poised to transform the DMD treatment landscape. This article explores the latest breakthroughs and trending therapies offering new possibilities for patients and their families.
The Promise of Genetic Therapies
Genetic therapies are at the forefront of innovative DMD treatments, targeting the underlying genetic defects responsible for the disease. These therapies aim to correct or compensate for the faulty dystrophin gene, which is crucial for muscle function.
Exon-Skipping Therapies
Exon-skipping is a technique designed to bypass defective exons in the dystrophin gene, allowing the production of a truncated but functional version of the dystrophin protein. Sarepta Therapeutics has been a pioneer in this field, with its drug eteplirsen (Exondys 51) approved by the FDA in 2016. Targeting exon 51, eteplirsen has shown the ability to increase dystrophin production, slowing disease progression. Building on this success, Sarepta has developed additional exon-skipping drugs, such as golodirsen (Vyondys 53) and casimersen (Amondys 45), each targeting different exons to treat a broader patient population.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy offers a revolutionary approach by delivering a functional copy of the dystrophin gene directly into muscle cells. Solid Biosciences and Pfizer are leading efforts in this domain. Solid Biosciences' SGT-001 and Pfizer's PF-06939926 are designed to introduce micro-dystrophin, a shortened but functional version of the dystrophin protein. Early clinical trial results for these therapies have shown promise, with improvements in muscle strength and function observed in treated patients.
CRISPR and Gene Editing
CRISPR-Cas9, a groundbreaking gene-editing technology, has opened new avenues for potentially curing genetic disorders like DMD. Researchers at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center achieved a significant milestone by using CRISPR to correct dystrophin gene mutations in a mouse model of DMD. This success paves the way for human clinical trials, with the potential to provide a permanent solution to the disease by repairing the defective gene at its source.
Anti-Sense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
Anti-sense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are short, synthetic strands of nucleic acids that can bind to specific RNA sequences, modulating gene expression. NS Pharma's viltolarsen (Viltepso) is an FDA-approved ASO therapy targeting exon 53, similar to golodirsen. Viltolarsen has demonstrated the ability to produce dystrophin in patients, offering another valuable option for those with specific genetic mutations.
Utrophin Modulation
Utrophin is a protein similar to dystrophin, and increasing its expression could compensate for the lack of dystrophin in DMD patients. Summit Therapeutics is developing ezutromid, a utrophin modulator aimed at upregulating utrophin production. Although early clinical trials showed promise, Summit discontinued ezutromid development due to disappointing later-stage results. However, the concept of utrophin modulation remains a viable therapeutic strategy, and ongoing research aims to identify more effective compounds.
Anti-Fibrotic and Anti-Inflammatory Therapies
Muscle fibrosis and inflammation are significant contributors to the progression of DMD. Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory therapies aim to mitigate these effects, preserving muscle function and delaying disease progression.
FibroGen's Pamrevlumab
Pamrevlumab is an anti-fibrotic agent developed by FibroGen, currently in clinical trials for DMD. By inhibiting connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), pamrevlumab aims to reduce muscle fibrosis, improving muscle function and overall outcomes for patients.
Catabasis Pharmaceuticals' Edasalonexent
Edasalonexent is an oral NF-kB inhibitor developed by Catabasis Pharmaceuticals. NF-kB is a protein complex that plays a key role in inflammation and muscle degeneration in DMD. Edasalonexent has shown potential in reducing inflammation and preserving muscle function in early clinical trials, although recent results have led to the discontinuation of its development for DMD.
Cellular Therapies
Cellular therapies involve the transplantation of healthy cells to replace damaged muscle cells in DMD patients. This approach aims to restore muscle function and halt disease progression.
Capricor Therapeutics' CAP-1002
CAP-1002 is a cardiac-derived cell therapy developed by Capricor Therapeutics, currently in clinical trials for DMD. These cells have shown the ability to reduce inflammation and improve muscle regeneration in preclinical studies. Early clinical results have been promising, suggesting potential benefits in preserving cardiac and skeletal muscle function.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form- php/?product_id=60948
The Role of Regulatory Agencies
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has played a crucial role in advancing DMD therapies through supportive regulatory frameworks. The FDA's orphan drug designation provides incentives such as tax credits and market exclusivity, encouraging pharmaceutical companies to invest in rare disease treatments. Additionally, the accelerated approval pathway allows for earlier approval of drugs based on surrogate endpoints, facilitating faster patient access to new therapies.
Patient Advocacy and Support
Patient advocacy groups have been instrumental in driving progress in DMD research and treatment. Organizations like Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD) and the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) have raised significant funds to support research initiatives, clinical trials, and patient care. Their advocacy efforts have also led to important policy changes, ensuring better access to treatments and resources for DMD patients.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the advancements in DMD therapies are promising, several challenges remain. The high cost of genetic and cellular therapies poses a significant barrier to accessibility. Ensuring these treatments are affordable and covered by insurance is crucial for widespread patient benefit. Additionally, long-term safety and efficacy data are needed to understand the impact of these therapies fully.
Looking ahead, continued investment in research and development, coupled with robust regulatory support and patient advocacy, will be essential in overcoming these challenges. The goal is to provide effective, accessible treatments that improve the quality of life and extend the lifespan of individuals with DMD.
Conclusion
The landscape of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy treatment is undergoing a transformative shift with the emergence of innovative therapies. From genetic and cellular therapies to anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory agents, these advancements offer hope for better management and potential cures for DMD. As the field continues to evolve, the collaboration between researchers, clinicians, regulatory agencies, and patient advocacy groups will be pivotal in driving further progress and ensuring all patients have access to life-changing treatments. The future holds promise for those affected by DMD, as emerging therapies pave the way for improved outcomes.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos Market Insights
Email - contact@univdatos.com
Contact Number - +1 9782263411
Website -www.univdatos.com