Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. With the rising incidence rates, particularly of melanoma, the role of dermatologists in skin cancer prevention has never been more critical. Dermatologists are not only experts in diagnosing and treating skin conditions but also play a vital role in educating patients about skin cancer risks, promoting prevention strategies, and ensuring early detection.
Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer primarily arises from the uncontrolled growth of skin cells, often caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. There are three main types of skin cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common form, typically appearing as a small, shiny bump or sore that doesn’t heal.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Often presenting as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore that crusts or bleeds.
- Melanoma: The most aggressive and dangerous form, characterized by changes in an existing mole or the appearance of new pigmented lesions.
The Role of Dermatologists
1. Education and Awareness
Dermatologists play a crucial role in educating the public about skin cancer risks and prevention strategies. This includes:
- Promoting Sun Safety: Dermatologists emphasize the importance of protective measures against UV exposure, such as wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing.
- Dispelling Myths: They help debunk common misconceptions about tanning and sun exposure, clarifying that a tan is not a sign of health and that there is no safe way to tan.
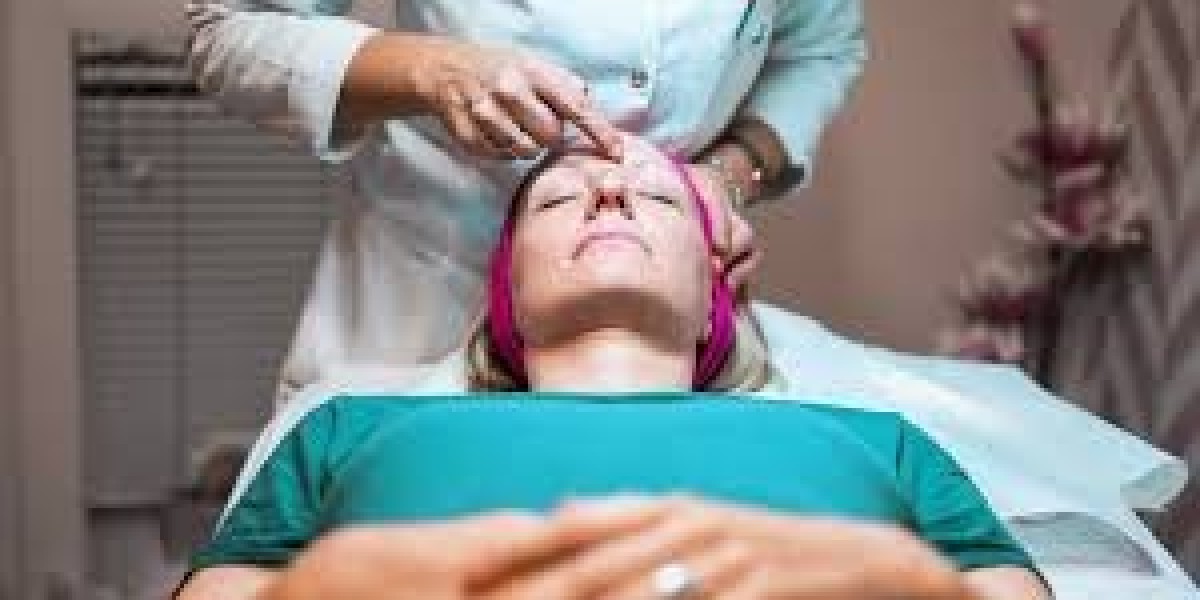
2. Regular Skin Examinations
Routine skin examinations are essential for early detection of skin cancer. Dermatologists recommend:
- Annual Check-Ups: Individuals, especially those with risk factors (e.g., fair skin, family history of skin cancer, or previous skin cancers), should have annual skin examinations.
- Self-Examinations: Dermatologists teach patients how to perform regular self-examinations to identify any new or changing moles or lesions.
3. Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection significantly improves the prognosis for skin cancer. Dermatologists utilize various methods to ensure timely diagnosis:
- Dermatoscopy: A specialized tool that allows dermatologists to examine skin lesions in greater detail, improving the accuracy of diagnoses.
- Biopsies: If a suspicious lesion is found, dermatologists may perform a biopsy to determine whether it is cancerous.
4. Treatment and Management
In cases of diagnosed skin cancer, dermatologists provide comprehensive treatment options, including:
- Surgical Excision: Removal of cancerous skin lesions, often with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal.
- Mohs Surgery: A precise surgical technique used to treat non-melanoma skin cancers, allowing for the conservation of healthy skin.
- Topical Therapies: Medications applied directly to the skin for superficial cancers or precancerous lesions.
5. Advocacy and Research
Dermatologists are also actively involved in advocating for skin cancer awareness and research. They participate in:
- Community Outreach Programs: Offering free skin cancer screenings, educational workshops, and awareness campaigns in the community.
- Research Initiatives: Engaging in clinical research to better understand skin cancer, develop new treatment modalities, and improve prevention strategies.
Conclusion
Dermatologists play a vital role in skin cancer prevention through education, early detection, and effective management. By promoting sun safety, conducting regular skin examinations, and advocating for awareness, dermatologists help reduce the incidence of skin cancer and improve outcomes for those affected. With their expertise and commitment to patient care, dermatologists are essential allies in the fight against skin cancer, ensuring that individuals are informed, proactive, and empowered to protect their skin health.