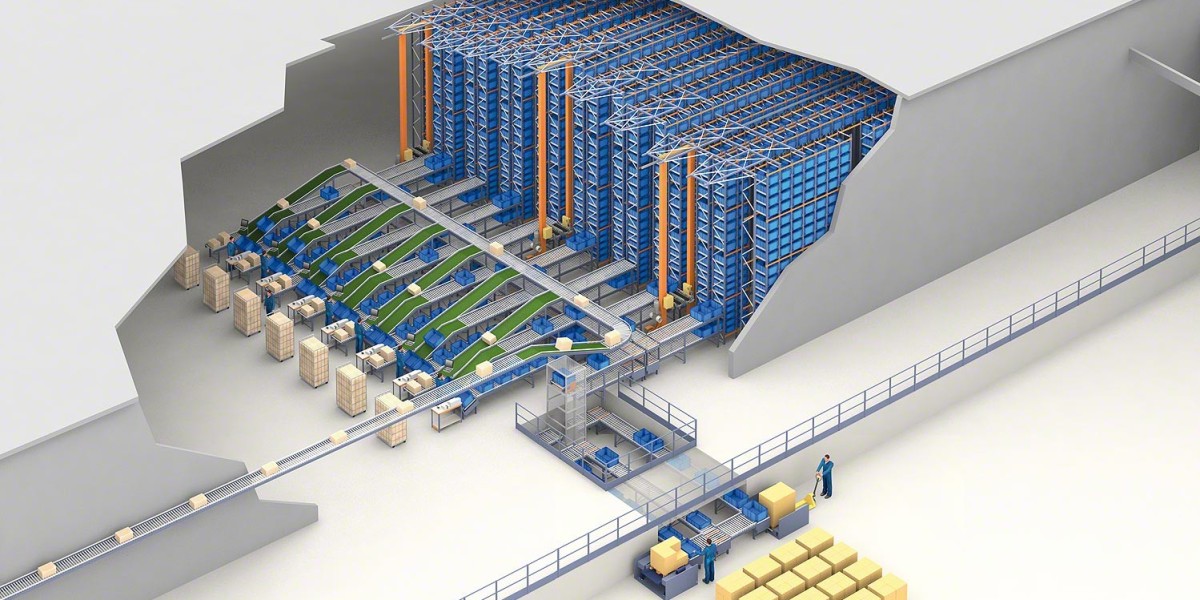
The warehouse automation market is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demands of modern supply chains. Automation solutions, including robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and advanced warehouse management systems (WMS), offer substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and speed. However, one of the most significant barriers to adoption remains the high initial investment required for these technologies. This article explores the challenges posed by these upfront costs and their impact on the warehouse automation market.
The Rising Demand for Automation
As e-commerce continues to surge, businesses are under immense pressure to enhance their logistics operations. Customers now expect faster delivery times, greater product availability, and improved service levels. In this context, warehouse automation presents an attractive solution. Automated systems can streamline processes, reduce labor costs, and minimize human error, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Despite these advantages, many organizations hesitate to invest in automation due to the substantial capital required. This hesitation can hinder progress in optimizing warehouse operations and responding to market demands.
Understanding High Initial Investments
1. Equipment Costs
One of the most significant contributors to the high initial investment in warehouse automation is the cost of equipment. Automated systems such as robotics, conveyors, and AS/RS require considerable financial outlay. The price tag for these technologies can vary widely based on factors such as the complexity of the system, the scale of the warehouse, and the specific requirements of the operation.
For smaller businesses or those operating on thin margins, the prospect of investing tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars in automation equipment can be daunting. This financial burden often leads to a cautious approach to automation, causing many companies to delay or forgo investments altogether.
2. Installation and Integration Costs
Beyond the purchase price of automation equipment, businesses must also consider the costs associated with installation and integration. Implementing new systems often requires significant modifications to existing infrastructure, which can add to the overall expenses. Integrating automated solutions with legacy systems and ensuring seamless communication between different technologies can be particularly challenging.
The need for specialized expertise during the installation phase may further increase costs. Many organizations opt to hire third-party consultants or service providers to manage the integration process, leading to additional expenditures that can stretch budgets.
3. Training and Change Management
Implementing warehouse automation solutions necessitates a cultural shift within the organization. Employees must adapt to new technologies, which often involves training programs to ensure they are equipped to operate and interact with automated systems effectively. Training costs can accumulate quickly, especially in larger warehouses where multiple staff members require instruction.
Moreover, change management is crucial for a successful transition to automation. Employees may be resistant to change, fearing job displacement or the challenges of learning new systems. Effective change management strategies are essential, but they often require additional resources, including time and financial investment.
4. Ongoing Maintenance and Support
After the initial investment, organizations must also consider the ongoing costs of maintaining and supporting automated systems. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure equipment operates efficiently and to prevent costly downtime. Maintenance contracts, spare parts, and technical support can add to the overall financial burden.
For businesses already stretched thin, these ongoing costs can be a deterrent to investing in automation. Organizations must carefully weigh the potential long-term benefits of automation against the continuous expenses associated with its upkeep.
Impact on Adoption Rates
The high initial investments required for warehouse automation have a notable impact on adoption rates, particularly among small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). While larger corporations often have the capital and resources to implement automation successfully, SMEs may struggle to justify the costs. This disparity can create a competitive disadvantage for smaller businesses, limiting their ability to optimize operations and compete effectively in the marketplace.
Furthermore, the reluctance to invest in automation can lead to a broader reluctance to innovate. Companies that do not embrace automation may find themselves falling behind as competitors leverage these technologies to enhance their operations and improve customer service.
Overcoming Investment Challenges
Despite the challenges associated with high initial investments, organizations can take several steps to overcome these barriers:
1. Evaluate Return on Investment (ROI)
Before committing to automation, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of the potential return on investment. By identifying the long-term cost savings, efficiency improvements, and revenue enhancements that automation can provide, organizations can make informed decisions about their investments.
2. Start Small
For organizations wary of making substantial upfront investments, starting with smaller automation projects can be a prudent approach. By implementing automation solutions in phases, businesses can gradually build their capabilities and assess the benefits before committing to larger-scale investments.
3. Seek Financial Assistance
Many governments and financial institutions offer grants, loans, or incentives to encourage businesses to adopt automation technologies. Organizations should explore available funding options to help alleviate the financial burden of initial investments.
4. Partner with Experts
Collaborating with technology providers or automation experts can streamline the implementation process and reduce costs. These partnerships can offer valuable insights, best practices, and support throughout the adoption journey, making it easier for organizations to integrate automation effectively.
5. Focus on Training and Change Management
Investing in training and change management initiatives can ease the transition to automation. By preparing employees for the changes ahead, organizations can reduce resistance and foster a culture of innovation and adaptability.
Conclusion
The warehouse automation market offers significant opportunities for businesses to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer service. However, the high initial investments associated with automation technologies pose a formidable challenge, particularly for smaller organizations. By understanding the factors contributing to these costs and exploring strategies to mitigate them, businesses can navigate the complexities of automation adoption. As the market continues to evolve, those that embrace automation while addressing investment challenges will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.