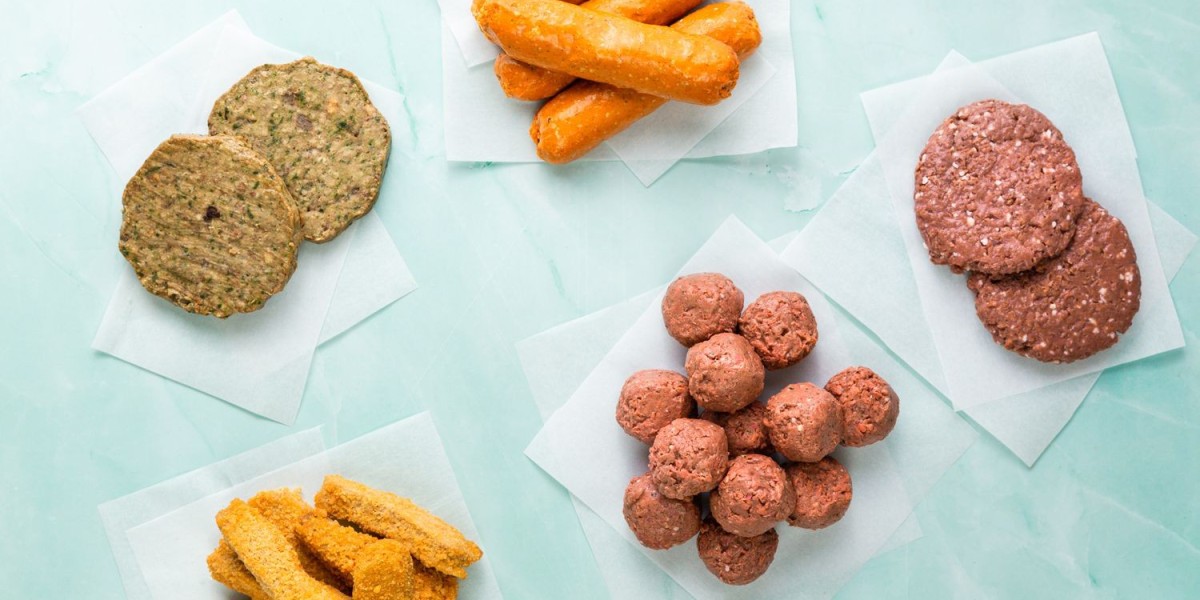
The plant-based meat market has emerged as a transformative force in the food industry, driven by changing consumer preferences and growing awareness of health, environmental, and ethical concerns associated with traditional meat consumption. This article explores the significance of the plant-based meat market, highlighting its impact on health, sustainability, economic opportunities, and the future of food production.
Health Benefits
One of the primary drivers of the plant-based meat market is the increasing awareness of health benefits associated with plant-based diets. Research has shown that diets rich in plant-based foods can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Plant-based meats are often lower in saturated fats and cholesterol compared to their animal-based counterparts, making them appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Moreover, many plant-based meat products are fortified with vitamins and minerals, providing a nutritious alternative for individuals looking to reduce or eliminate meat from their diets. As more people adopt flexitarian or vegetarian lifestyles, the demand for nutritious and convenient plant-based options continues to rise.
Environmental Sustainability
The significance of the plant-based meat market extends beyond individual health; it also encompasses broader environmental concerns. The livestock industry is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water consumption. By reducing reliance on animal agriculture, plant-based meat alternatives offer a more sustainable solution for food production.
Studies suggest that transitioning to plant-based diets could lead to substantial reductions in environmental impact, including a decrease in land and water usage and lower carbon emissions. As consumers become increasingly aware of climate change and its implications, the demand for sustainable food options is expected to grow. The plant-based meat market provides a viable pathway toward a more sustainable food system, addressing pressing global challenges.
Economic Opportunities
The growth of the plant-based meat market also presents significant economic opportunities. As consumer demand increases, so does the potential for innovation and job creation within this sector. Startups and established companies alike are investing heavily in research and development to create new and improved plant-based products. This investment fosters innovation, leading to a wider variety of options that cater to diverse tastes and dietary preferences.
Furthermore, the expansion of the plant-based meat market is contributing to a shift in agricultural practices. Farmers are increasingly diversifying their crops to include legumes, grains, and other plant-based ingredients used in meat alternatives. This diversification not only supports sustainable agriculture but also provides farmers with new revenue streams.
The Future of Food Production
The significance of the plant-based meat market is also tied to the future of food production. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food will increase, placing further strain on the environment and food systems. Plant-based meats offer a scalable solution to meet this demand without exacerbating existing challenges related to climate change, resource depletion, and food security.
Innovations in food technology, such as cell-based meat and improved plant protein extraction methods, are likely to enhance the quality and variety of plant-based products. As these technologies advance, they could lead to even greater acceptance of plant-based meats among mainstream consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the significance of the plant-based meat market lies in its potential to promote health, support environmental sustainability, create economic opportunities, and shape the future of food production. As consumers increasingly prioritize health and sustainability, the plant-based meat market is positioned for continued growth and innovation. By embracing this shift, stakeholders can contribute to a more sustainable and equitable food system that benefits individuals, communities, and the planet.