The aquaculture feed market is undergoing significant transformations driven by various dynamic forces. As global demand for seafood continues to rise, the industry faces pressure to innovate and adopt more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective practices. This article explores the key forces shaping the future of the aquaculture feed market, from technological advancements to changing consumer preferences and environmental concerns.
1. Rising Global Demand for Seafood
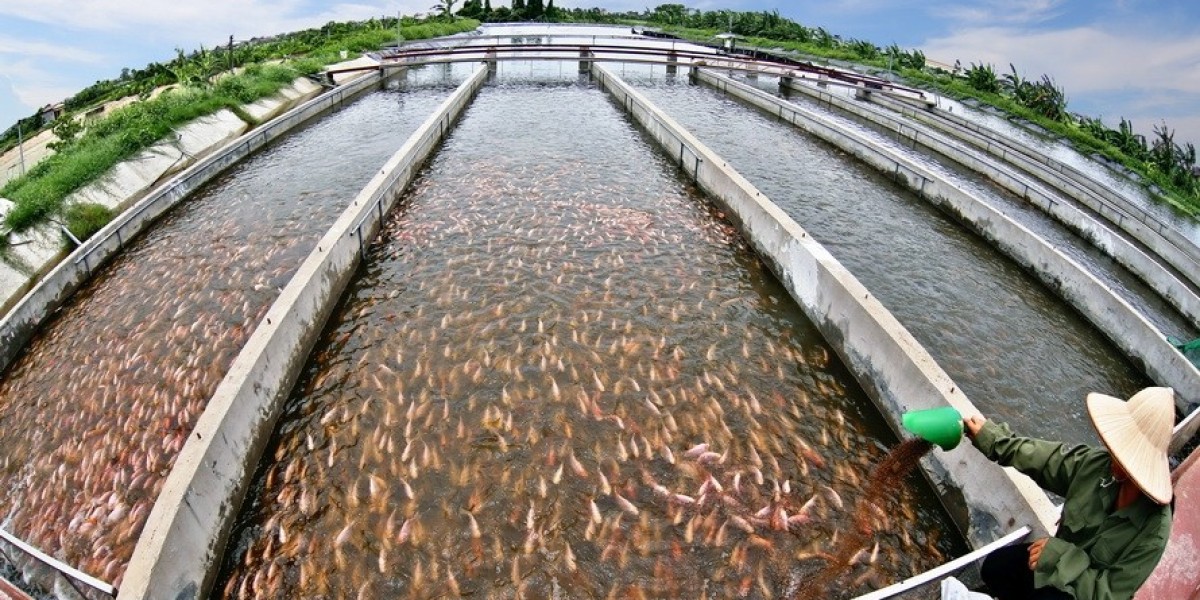
One of the most influential drivers of the aquaculture feed market is the increasing global demand for seafood. As the global population grows and dietary patterns shift, more consumers are turning to seafood as a primary protein source, pushing aquaculture production to new heights. This surge in demand is creating a direct need for high-quality feed to support the growing number of aquaculture farms worldwide.
Key Dynamics:
Health and Nutritional Benefits: With rising awareness of the health benefits associated with seafood—such as high protein content, omega-3 fatty acids, and lower fat content—consumers are prioritizing seafood in their diets. As this trend continues, the demand for farmed fish will continue to increase, thereby driving the need for efficient and scalable feed solutions.
Sustainable Protein Source: Aquaculture is viewed as a more sustainable alternative to terrestrial animal farming, which has a larger environmental footprint. As a result, governments and businesses are pushing for the expansion of aquaculture to meet protein demand, which, in turn, increases the need for quality feed.
2. Technological Advancements in Feed Production
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping the future of the aquaculture feed industry. Innovations in feed formulation, processing techniques, and production efficiency are enabling feed manufacturers to create more effective, sustainable, and economically viable feed products.
Key Dynamics:
Precision Feeding Systems: The development of automated and precision feeding systems has transformed the way aquaculture farms manage their feed. These systems use sensors, AI, and data analytics to deliver the right amount of feed at the right time, minimizing waste and optimizing feed conversion ratios (FCR). This technology not only improves fish health but also reduces environmental impacts by lowering feed waste and optimizing resource use.
Smart Feed Solutions: Advances in smart feed formulations that adapt to the specific needs of different fish species are becoming more common. These feeds are designed to release nutrients gradually, based on the fish’s growth stage or environmental conditions, ensuring optimal nutrition while reducing feed waste.
Alternative Ingredients: The search for alternative protein sources, such as insect meal, algae, and plant-based proteins, is gaining momentum. These innovations are reducing the dependence on traditional fishmeal, which is both costly and environmentally taxing, thus making feed production more sustainable and affordable.
3. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is one of the most pressing issues in the aquaculture feed market. As the aquaculture industry expands, it faces increasing scrutiny from consumers, environmental groups, and governments regarding its environmental footprint. In response, the industry is shifting towards more sustainable feed practices.
Key Dynamics:
Alternative Proteins and Ingredients: The use of alternative feed ingredients, such as plant-based proteins, insect meal, and algae, is gaining traction as a way to reduce the environmental impact of feed production. These ingredients not only provide a sustainable protein source but also help reduce the industry's reliance on wild-caught fish, which are overexploited and increasingly scarce.
Circular Economy: The concept of a circular economy, where waste from one process becomes input for another, is being applied in the aquaculture feed industry. By using by-products from other sectors (such as agriculture or food processing), feed manufacturers can create more sustainable and resource-efficient feed solutions.
Reduction of Carbon Footprint: In line with global sustainability goals, the aquaculture industry is focusing on reducing its carbon footprint. This involves optimizing feed production methods, sourcing more sustainable ingredients, and adopting eco-friendly processing technologies.
4. Regulatory Pressure and Industry Standards
As sustainability concerns grow, so does the pressure from governments and regulatory bodies for aquaculture farms and feed manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. This regulatory environment is pushing the industry towards greater transparency, traceability, and accountability in feed production.
Key Dynamics:
Stricter Environmental Regulations: Governments across the world are introducing stricter environmental standards for aquaculture production, particularly in terms of feed ingredients and production processes. For example, some countries are placing limits on the amount of fishmeal and fish oil that can be used in aquaculture feed, pushing the industry to seek out more sustainable alternatives.
Certification and Labeling: Certifications like the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) are becoming increasingly important for feed manufacturers. These certifications ensure that the feed is sourced responsibly and that aquaculture operations meet sustainable standards. This trend is pushing the industry to invest in traceability and sustainable sourcing practices.
Government Subsidies and Support: Some governments offer subsidies or grants for aquaculture companies that adopt environmentally friendly practices, including the use of sustainable feed ingredients. This creates an opportunity for feed manufacturers to innovate in line with regulatory demands while benefiting from financial incentives.
5. Consumer Trends and Demand for Transparency
Consumer behavior is shifting toward more sustainable, traceable, and ethically produced food. As a result, aquaculture feed manufacturers are being pushed to align their products with these growing consumer expectations.
Key Dynamics:
Demand for Clean Label Products: Consumers are increasingly looking for clean-label products, meaning they want food with minimal additives and transparent sourcing. This trend extends to aquaculture, where consumers are demanding seafood produced using sustainable and traceable feed ingredients. Feed manufacturers are responding by developing products that meet these clean-label criteria.
Traceability and Blockchain: The growing demand for transparency in the food supply chain is prompting the integration of technologies like blockchain to track feed ingredients from farm to plate. Blockchain can provide consumers with verifiable proof of where feed ingredients are sourced, ensuring that they are ethically and sustainably produced.
Plant-Based and Non-GMO Feeds: With an increasing number of consumers opting for plant-based diets and non-GMO foods, there is a growing market for non-GMO and plant-based aquaculture feed. Feed producers are tapping into this trend by developing feeds that align with the preferences of health-conscious consumers.
6. Increasing Aquaculture Production in Emerging Markets
The rapid expansion of aquaculture in emerging markets is another key driver of the aquaculture feed market. Countries in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are investing heavily in aquaculture to meet the rising demand for protein, creating significant opportunities for feed producers.
Key Dynamics:
Aquaculture Growth in Asia: Asia-Pacific, particularly countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, continues to be the largest producer and consumer of aquaculture products. The demand for feed in this region is expected to grow as fish farming continues to expand.
Aquaculture Development in Africa and Latin America: Emerging economies in Africa and Latin America are beginning to invest in aquaculture as a solution to food security and economic growth. As these regions increase their aquaculture production, there will be a rising demand for affordable, efficient, and sustainable feed solutions.
Local Ingredient Sourcing: As aquaculture production grows in emerging markets, there is an opportunity to use locally available feed ingredients, reducing costs and improving food security. Local sourcing can also improve the sustainability of feed production by reducing transportation and supply chain emissions.
7. Economic Factors and Market Competition
Economic factors, including feed ingredient prices, global trade policies, and market competition, significantly influence the dynamics of the aquaculture feed market. These factors can either spur innovation or pose challenges to feed manufacturers.
Key Dynamics:
Fluctuating Raw Material Prices: The cost of raw materials, particularly fishmeal and fish oil, is highly volatile and depends on global supply and demand. This affects the pricing of aquaculture feed and drives feed manufacturers to find more cost-effective alternatives to traditional ingredients.
Global Trade and Supply Chain Challenges: Trade policies, tariffs, and global supply chain disruptions can impact the availability and cost of feed ingredients. This has led to an increased focus on local sourcing and regional supply chains to mitigate risks.
Competitive Landscape: The aquaculture feed market is highly competitive, with numerous players striving to differentiate themselves through product quality, sustainability practices, and technological innovations. This intense competition encourages continuous improvement and innovation across the industry.