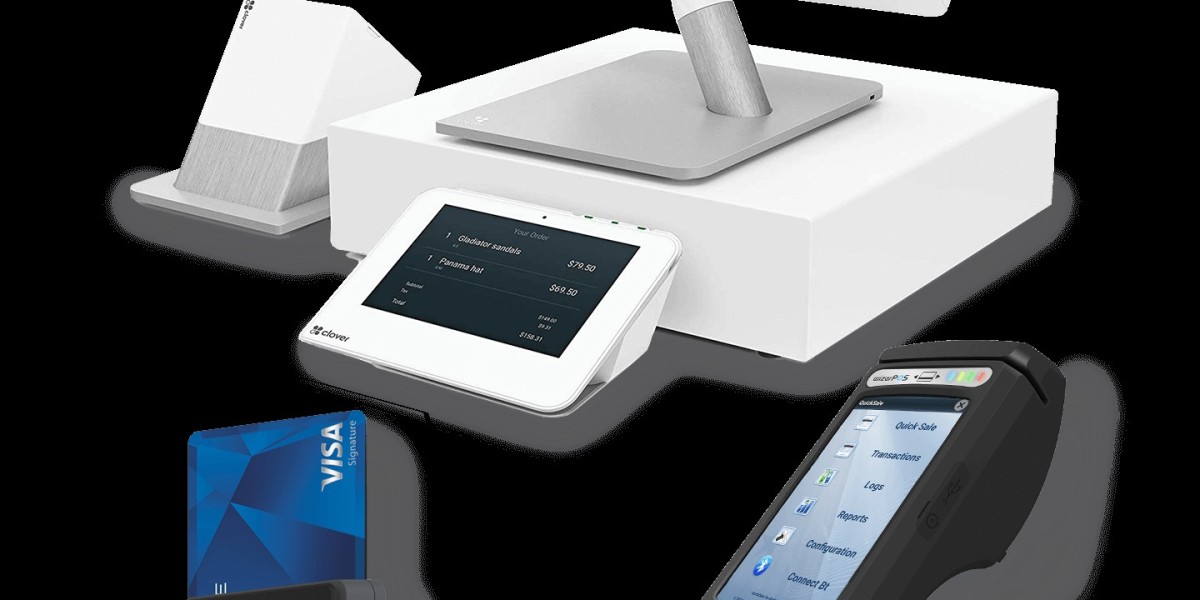
Merchant credit card processor plays a crucial role in modern commerce. They enable businesses to accept credit and debit card payments efficiently, streamlining the purchasing experience for customers. With various options available, choosing the right merchant services provider can significantly impact transaction speed, security, and overall customer satisfaction.
Understanding the features and fees associated with different processors is essential for any business owner. From point-of-sale systems to online payment gateways, each solution offers unique benefits tailored to specific business needs. This knowledge empowers entrepreneurs to make informed decisions that will enhance their operations.
As payment methods continue to evolve, staying updated on the latest trends and technologies in merchant services is vital. Exploring the nuances of these services allows businesses to remain competitive and meet the changing preferences of their customers.
Understanding Merchant Credit Card Processing
Merchant credit card processing is essential for businesses that accept card payments. It involves several components that ensure secure transactions and effective management of funds.
The Role of Merchant Services
Merchant services encompass a variety of financial services that enable businesses to accept credit card payments. These services include payment processing, transaction reporting, and fraud protection.
Key components include:
- Transaction Processing: This facilitates the approval or decline of credit card transactions.
- Payment Gateway: A service that authorizes payments and ensures data security during transmission.
- Merchant Account: A specialized bank account that allows businesses to accept card payments and hold funds until they are transferred to a business's operating account.
Merchant service providers often offer additional resources, such as analytics tools and customer support.
How Credit Card Processing Works
Credit card processing involves a series of steps to complete a transaction. It begins when a customer presents their card for payment.
- Authorization: The payment is initiated, and the card details are sent to the acquiring bank.
- Verification: The bank checks if the funds are available and sends the authorization back to the merchant.
- Transaction Completion: Once authorized, the sale is finalized, and the customer receives a receipt.
- Settlement: Funds are transferred from the customer’s bank to the merchant's account, which typically takes a few days.
This process relies on secure communications to protect sensitive customer data throughout the transaction.
Types of Merchant Services Providers
Merchant services providers vary widely, catering to different business needs. They can be classified into three main types:
- Traditional Banks: Many offer merchant services as part of their business banking solutions, often providing reliable service and a familiar setup.
- Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs): These are third-party companies that partner with banks to offer tailored services, frequently with lower fees and flexible contracts.
- Payment Processors: Specialized companies focused solely on processing payments. They can provide advanced features like mobile payments and integrated point-of-sale systems.
Choosing the right provider depends on the specific requirements of the business and the types of services offered.
Selecting a Merchant Services Credit Card Processor
When selecting a merchant services credit card processor, it's essential to consider factors such as fees, security, integrations, and support. The right choice can significantly impact a business's operations and customer satisfaction.
Evaluating Processing Fees and Costs
Processing fees can significantly affect a business's bottom line. Merchants should review various fee structures that processors offer. Common fees include transaction fees, monthly fees, and chargeback fees.
- Transaction Fees: Usually a percentage of the sale, this fee can vary widely.
- Monthly Fees: These are fixed costs for maintaining the account, which may include service charges.
- Setup Fees: Some processors charge a one-time fee for account setup.
Merchants should compare these fees against their sales volume to determine the most cost-effective option. A processor that seems cheaper initially may impose hidden fees that diminish savings.
Security and PCI Compliance
Security is crucial in the payment processing landscape. Merchants must ensure that their processor adheres to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS). Compliance protects sensitive customer data and builds trust.
Key points to review include:
- Encryption Techniques: Ensuring data is encrypted during transactions can prevent breaches.
- Data Storage Policies: Understanding how transaction data is stored and for how long helps mitigate risks.
- Fraud Prevention Tools: Many processors offer tools to help identify potentially fraudulent transactions.
Adopting a processor with robust security measures can safeguard a business's reputation and customer trust.
Assessing Payment Gateway Integrations
A payment processor's ability to integrate with existing systems is vital for smooth operations. Integrations should be compatible with eCommerce platforms, accounting software, and point-of-sale systems.
Merchants must consider:
- Supported Platforms: Check if the processor works seamlessly with popular platforms.
- API Availability: An open API can provide flexibility in customization.
- Ease of Integration: The simpler the integration process, the quicker a business can start processing payments.
Effective integration contributes to efficient transaction handling and financial management.
Customer Support and Service Considerations
Quality customer support can greatly influence a merchant's experience with a processor. Timely and effective assistance is necessary for resolving transaction issues or technical problems.
Merchants should evaluate:
- Availability of Support: Determine if support is available 24/7 or during business hours only.
- Communication Channels: Check if support is accessible via phone, email, or live chat.
- Response Times: Understanding typical response times can indicate the reliability of the support team.
A processor with strong customer service can enhance a merchant's experience and confidence in their payment processing partner.