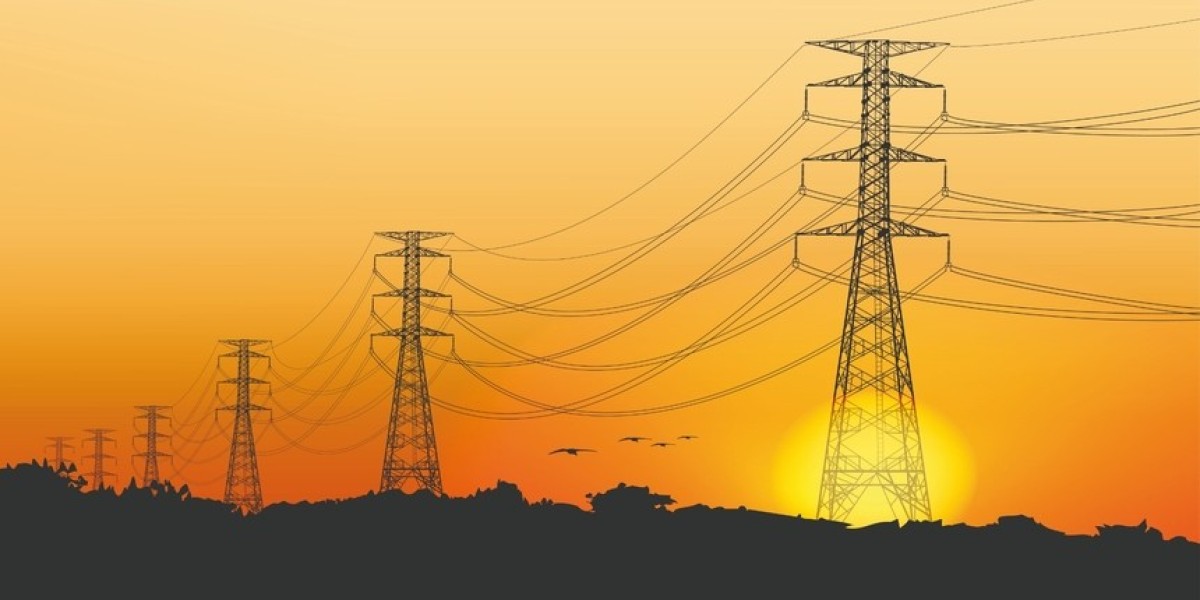
The electricity transmission infrastructure market is undergoing significant transformation as the world moves towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. However, challenges related to outdated infrastructure, integration of renewable energy, financing, and geopolitical concerns remain. This article explores the challenges faced by the market and discusses potential strategies to address them while ensuring future growth and sustainability.
1. Aging Infrastructure and Maintenance Costs
One of the biggest challenges facing the electricity transmission infrastructure market is the aging of existing transmission lines and substations. In many regions, especially in developed economies, much of the infrastructure is decades old and is prone to inefficiencies and failures.
- High Maintenance Costs: Maintaining and upgrading outdated systems is costly, diverting resources away from new projects and developments. Aging infrastructure also leads to increased transmission losses, affecting overall grid efficiency.
- Infrastructure Modernization: Addressing the aging infrastructure requires significant investment in modernization, including replacing old lines, substations, and transformers. This is a critical challenge, particularly in regions where budget constraints limit the pace of these upgrades.
2. Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Stability
The integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar presents another major challenge to electricity transmission infrastructure. Unlike conventional energy sources, renewables are intermittent and geographically dispersed, which can make it difficult to maintain grid stability.
- Intermittency of Renewable Energy: The variability in renewable energy production—due to weather patterns, time of day, and seasons—can cause fluctuations in supply and demand. Ensuring that these fluctuations do not destabilize the grid requires advanced technologies and additional infrastructure.
- Upgrading the Grid: To manage renewable energy’s intermittency, grids must be upgraded to incorporate energy storage solutions, flexible transmission systems, and advanced control technologies. This requires both significant technological innovation and financial investment.
3. Financing and Investment Constraints
Financing the development and upgrade of electricity transmission infrastructure is often a significant barrier. The capital-intensive nature of these projects, combined with long timelines for returns on investment, deters private investors and complicates public funding efforts.
- Funding Challenges: Many emerging and developing economies face difficulty in securing the necessary funds to modernize transmission infrastructure, which can stymie overall market growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): One potential solution is fostering public-private partnerships (PPPs), where governments and private companies collaborate on funding and executing transmission projects. These partnerships can help mitigate the financial burden on governments while attracting private sector expertise and investment.
4. Regulatory and Policy Challenges
Regulatory uncertainty and policy fragmentation can create additional hurdles in the electricity transmission infrastructure market. Changes in government policies, fluctuating regulatory environments, and inconsistent regulations across regions can complicate investment decisions and slow down project implementation.
- Uncertain Policy Environment: Shifting energy policies, such as changes in renewable energy targets or emission reduction laws, can create uncertainty for investors and developers.
- Policy Alignment: Governments need to establish clear, consistent, and long-term policies to provide stability for investors and ensure the successful implementation of transmission infrastructure projects. This includes setting clear guidelines for integrating renewable energy, incentivizing grid modernization, and encouraging technological innovation.
5. Cybersecurity Threats and Technological Vulnerabilities
With the increasing use of digital technologies in electricity transmission systems, cybersecurity has become a growing concern. Transmission infrastructure is becoming more connected and automated, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can disrupt grid operations and threaten energy security.
- Vulnerabilities in Smart Grids: While smart grids offer improved efficiency and control, they also introduce new vulnerabilities. Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure, such as substations and transmission lines, can lead to system failures or even catastrophic blackouts.
- Cybersecurity Investments: Protecting electricity transmission systems from cyber threats requires significant investment in advanced cybersecurity measures, including robust encryption, intrusion detection systems, and constant monitoring of grid operations.
6. Geopolitical and Environmental Challenges
Geopolitical factors and environmental concerns also play a significant role in the development and operation of electricity transmission infrastructure. The global nature of energy trade and transmission means that political tensions, natural disasters, and environmental regulations can impact the reliability and efficiency of transmission networks.
- Cross-Border Transmission Projects: Many regions, particularly in Africa and Asia, are working on cross-border transmission projects. These projects can face delays or increased costs due to geopolitical tensions, regulatory differences, or local opposition.
- Climate Change Risks: Extreme weather events, such as floods, storms, and wildfires, are becoming more frequent and can damage transmission infrastructure. These risks are heightened in regions that lack resilient infrastructure or are ill-prepared for climate-related events.
Future Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
1. Adoption of Advanced Transmission Technologies
To address the challenges of renewable energy integration and grid stability, advanced transmission technologies are essential. High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems, for example, are highly effective in transmitting renewable energy over long distances with minimal loss. Additionally, smart grid technologies, energy storage, and automated control systems can improve grid flexibility and resilience.
- Grid Modernization: Upgrading the grid with real-time monitoring systems, automated control mechanisms, and predictive maintenance capabilities can ensure smoother integration of renewable energy and improve grid stability.
2. Strengthening Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
To address financing constraints, it is crucial to foster stronger public-private partnerships. Governments can offer incentives, subsidies, and risk-sharing mechanisms to attract private investment in transmission infrastructure.
- International Financing: In developing economies, international financial institutions and development banks can play a crucial role in providing the necessary funding for large-scale transmission projects, especially those involving renewable energy integration.
3. Improving Regulatory Frameworks
Governments should focus on creating stable, long-term policies that align with energy transition goals. Clear regulations that encourage renewable energy development, grid modernization, and energy storage solutions will provide investors with the confidence to invest in transmission infrastructure.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: Regional cooperation between governments can help overcome regulatory challenges in cross-border electricity transmission projects. Harmonizing policies and regulations across countries will facilitate smoother and faster project development.
4. Enhancing Cybersecurity
As digital technologies continue to play a bigger role in electricity transmission systems, it is essential to invest in robust cybersecurity measures. Governments and private sector players must work together to develop and implement cybersecurity standards to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Training and Awareness: In addition to technology investments, training programs for grid operators and regular cybersecurity audits can help minimize vulnerabilities and mitigate risks.
Final Thoughts
The electricity transmission infrastructure market faces several challenges, including aging infrastructure, the integration of renewable energy, financing constraints, regulatory complexities, and cybersecurity risks. Addressing these challenges will require a combination of advanced technologies, policy reforms, and strategic investments. Governments, private investors, and utilities must collaborate to develop sustainable, resilient transmission systems that can meet future energy demands while supporting the global transition to clean energy.