The Industrial Heat Pump market represents an emerging and dynamic opportunity for manufacturers, energy providers, and businesses seeking cost-efficient, sustainable, and energy-saving solutions. With the increasing global demand for green technologies and the pressing need to lower carbon footprints, industrial heat pumps are playing a crucial role in the revolution of the industrial sector. By harnessing waste heat and integrating renewable energy into various manufacturing processes, heat pumps present a practical solution that addresses both sustainability and operational efficiency. This blog explores the potential of the Industrial Heat Pump market, factors driving growth, and challenges that might emerge in this space.
Introduction to Industrial Heat Pumps:
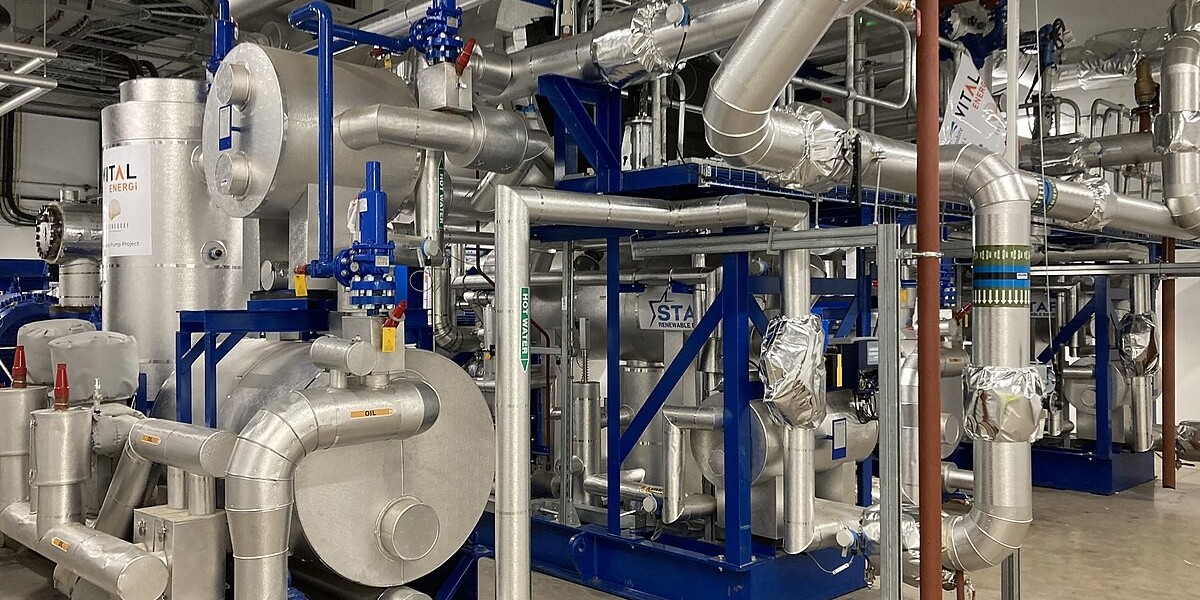
An industrial heat pump is a mechanical device that transfers heat from a lower temperature source (air, water, or ground) to a higher temperature destination, providing heating, cooling, and hot water in industrial applications. Heat pumps work efficiently by utilizing ambient energy to lower reliance on traditional heating sources like boilers, thereby significantly reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. For industries like food processing, chemical manufacturing, and metal production, the adoption of heat pumps could transform existing infrastructure, driving down costs while adhering to the growing environmental regulations.
Market Drivers:
The rapid acceleration of industrial growth combined with a global push toward carbon neutrality has generated significant attention in the Industrial Heat Pump market. The major drivers shaping the demand for industrial heat pumps include:
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: A primary advantage of industrial heat pumps lies in their remarkable energy efficiency. They can achieve heat transfer at a rate three to five times higher than traditional heating systems. As governments around the world impose stricter energy consumption guidelines and carbon regulations, industries are increasingly looking for alternative technologies that contribute to their sustainability goals.
Regulatory Pressures: Stringent environmental regulations such as the European Union's Green Deal and similar initiatives in other regions are encouraging industries to explore cleaner, energy-efficient alternatives. With an ever-decreasing focus on fossil fuels, these laws push the industrial sector to adopt technologies like heat pumps that reduce emissions and support overall environmental initiatives.
Waste Heat Utilization: Many industrial facilities emit large volumes of waste heat, which are either released into the environment or used inefficiently. Heat pumps can capture and repurpose waste heat, redirecting it back into production processes or for heating purposes. By doing so, industries can optimize energy use and reduce operational costs while simultaneously advancing toward a more circular economy.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Although the initial cost of implementing industrial heat pumps may seem high, the long-term savings associated with their energy-efficient operation make them an economically viable investment. The considerable reduction in energy consumption over time can offset the upfront installation costs, offering industries a faster return on investment.
Advancement in Technology: Technological advancements have led to improved performance and accessibility of industrial heat pumps. Enhanced designs, better refrigerant fluids, and smarter controls have expanded their applicability across different industries, ensuring that both large-scale and smaller industrial facilities can benefit from adopting this technology.
Challenges:
While the potential for growth in the industrial heat pump market is abundant, certain barriers must be addressed for widespread adoption:
High Initial Investment: Despite long-term savings, the initial upfront costs can be a significant hurdle for some industries, especially in economies or sectors that are cost-sensitive. Financial incentives or support from government programs are crucial to overcome this limitation.
Compatibility with Existing Systems: Integrating heat pumps with existing heating systems can sometimes be challenging, requiring substantial retrofitting of existing infrastructure. This can be costly and may slow down the pace at which industries switch to heat pumps.
Lack of Awareness and Knowledge: The industrial sector often operates with established technologies and processes. Convincing industrial players to switch to newer solutions like heat pumps requires addressing knowledge gaps and demonstrating clear, tangible benefits.
Looking to the Future:
The future of the industrial heat pump market looks highly promising. With growing focus on energy conservation, sustainability, and cutting-edge technological innovation, heat pumps are poised to play a pivotal role in the decarbonization of industrial processes. As awareness increases and cost structures evolve, businesses are likely to adopt heat pumps in greater numbers, contributing to a more sustainable and economically viable industrial ecosystem.
Governments and regulators are also expected to provide increased support for adopting energy-efficient systems, and with rising operational costs tied to energy usage, industries will continue seeking cost-effective alternatives. The market is likely to witness further integration with renewable energy systems, driving new synergies and opportunities for industrial innovation.
Conclusion:
The industrial heat pump market presents significant growth potential, driven by the need for energy-efficient solutions and compliance with increasingly strict environmental regulations. By reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and fostering sustainability, industrial heat pumps offer substantial benefits. However, the challenges related to investment costs and system integration should not be overlooked. With continuous advancements in technology and greater industry awareness, heat pumps will increasingly establish themselves as an essential component of sustainable industrial growth. As industries adopt greener practices, the market will continue to grow, creating ample opportunities for companies and consumers alike to enjoy the economic and environmental advantages these systems offer.