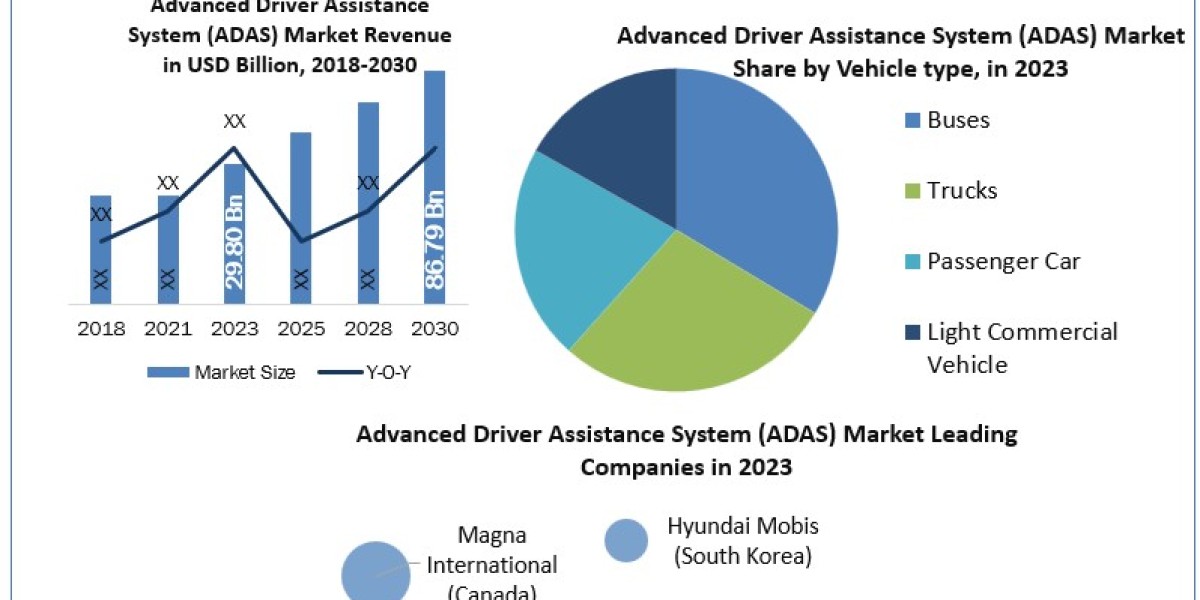
The electric vehicle (EV) charging station market is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing demand for clean transportation. However, despite the momentum and favorable governmental policies, several inhibitors hinder the industry's expansion. These challenges range from infrastructure limitations to financial and technological concerns. Understanding the primary inhibitors affecting the growth of the EV charging station market is crucial for businesses, governments, and investors aiming to navigate these obstacles.
1. Infrastructure Limitations
One of the biggest challenges faced by the electric vehicle charging station market is the lack of sufficient infrastructure. Although the number of EV charging stations is rising, it still falls short in many urban, suburban, and rural areas. Charging stations are concentrated in certain regions, mainly in larger cities and along highways, which limits EV adoption in more remote locations. Expanding infrastructure requires significant investment, technical expertise, and long-term planning to ensure a nationwide or global network.
2. High Initial Investment and Operational Costs
The high upfront cost required to build, operate, and maintain EV charging stations is another inhibitor to market growth. Establishing a charging station, especially fast-charging units, demands heavy capital investments in equipment, land, and labor. Additionally, maintenance and electricity costs for the stations also add up. Despite the lower operating costs over time, the high capital requirements deter some companies from entering the market, especially small and medium-sized businesses.
3. Technological Limitations
The development of high-speed, universally compatible charging solutions is still an ongoing challenge. Many electric vehicles use different charging standards, such as DC fast charging or AC charging, which means that charging stations often need to be equipped with multiple types of chargers to meet the needs of a broad range of EVs. The lack of standardization creates interoperability issues and complicates the deployment of EV charging infrastructure. Moreover, most charging stations require constant updates and upgrades to meet evolving technical standards.
4. Lack of Consumer Awareness
While electric vehicles are becoming more popular, many consumers are still unsure about EV charging stations. This lack of awareness stems from insufficient knowledge about how these stations work, their locations, and their availability. As a result, potential EV buyers may hesitate to make the switch from gasoline-powered vehicles, worrying about the convenience and accessibility of charging stations. Public education and marketing are essential to fostering consumer trust and encouraging the widespread adoption of EVs.
5. Energy Grid Limitations and Sustainability Concerns
The energy grid's capacity to handle the increased demand for electricity due to electric vehicle charging is another inhibitor. In some regions, energy grids are not yet prepared to manage large-scale electric vehicle integration without significant upgrades. There are also concerns regarding the environmental impact of increased electricity consumption. For an EV charging network to be genuinely sustainable, it must rely on renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. The transition to a fully sustainable and eco-friendly grid requires substantial investment and cooperation between governments, private companies, and energy providers.
6. Policy and Regulatory Challenges
While many governments are providing incentives and subsidies for the installation of EV charging stations, regulatory uncertainties still remain a barrier. Different countries and regions have varying laws regarding the installation, operation, and pricing of charging stations. This lack of uniformity makes it difficult for companies to plan and expand operations. Additionally, policy changes, such as shifts in government subsidies or tax credits, can greatly impact profitability, further discouraging investment in the sector.
7. Competition from Alternative Fuels and Charging Technologies
While the EV market is undoubtedly growing, it is also facing competition from other alternative fuels such as hydrogen and biofuels. Moreover, advancements in wireless charging technologies could potentially disrupt the conventional charging infrastructure. These evolving technologies may pose additional hurdles for the widespread adoption of electric vehicle charging stations, as they introduce new complexities, costs, and competition in an already highly competitive market.
Conclusion
The electric vehicle charging station market holds immense promise, but its growth is hampered by several inhibitors that must be addressed. Solving these challenges requires collaboration between private enterprises, governments, and consumers. While technological innovation and policy support are crucial to overcoming infrastructure, financial, and operational barriers, an integrated and forward-thinking approach will be key to fostering the long-term success of the EV charging network.