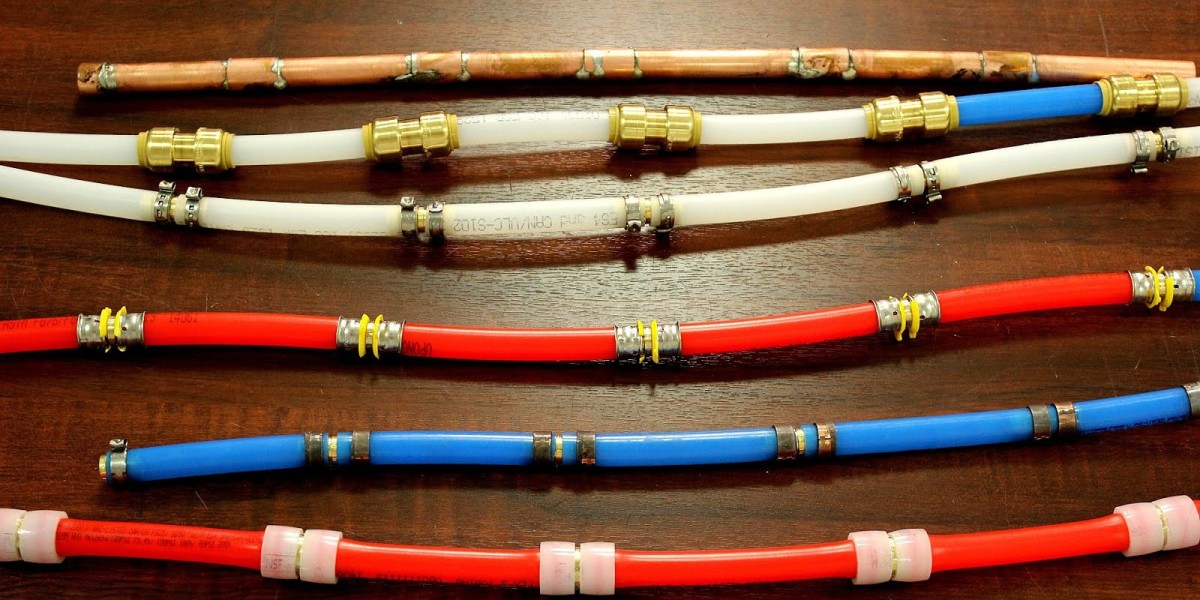
While the cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) market is experiencing notable growth, it faces several challenges that could impact its expansion. These restraints, which include material limitations, regulatory concerns, and competition from alternative solutions, are important factors for stakeholders to consider when navigating the market.
One of the primary restraints is the cost of production. Despite PEX’s numerous advantages, the manufacturing process, particularly the cross-linking stage, can be more expensive compared to other materials like PVC or traditional metals. The additional costs associated with specialized production techniques can lead to higher prices for end consumers, which may limit its adoption in price-sensitive markets or projects.
Another challenge is the material's susceptibility to UV degradation. While PEX is highly durable in many environments, prolonged exposure to sunlight can weaken the material, limiting its use in outdoor applications unless additional protective layers or coatings are applied. This restriction can reduce its versatility in certain construction and industrial projects.
The lack of standardization across regions also presents a challenge for the global adoption of PEX. In some areas, building codes and regulations may not yet fully recognize PEX as a viable alternative to traditional materials, hindering its widespread use. Furthermore, varying quality standards and inconsistent product offerings can create uncertainty for consumers and industries looking to adopt PEX-based solutions.
Lastly, competition from alternative materials like copper, PVC, and newer materials like multilayer composite pipes also poses a challenge. These materials often have established supply chains and lower production costs, making it difficult for PEX to compete in certain markets.
In summary, while the cross-linked polyethylene market holds significant promise, factors such as cost, material limitations, and regulatory challenges may slow its widespread adoption and growth.