Introduction
Acetyl chloride is an important chemical used primarily as a reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of acetates, which are widely used in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and plastic industries. Acetyl chloride is also used to produce acetylated cellulose, fragrances, and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various chemicals. Given its versatile applications, establishing an Acetyl Chloride Manufacturing Plant presents a profitable opportunity for businesses in the chemicals sector. The growing demand for acetyl chloride in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and synthetic materials has created significant opportunities for manufacturers to capitalize on this need. This Acetyl Chloride Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the necessary steps, equipment, raw materials, and financial considerations for setting up a manufacturing facility dedicated to the production of acetyl chloride.
Acetyl Chloride Manufacturing Process
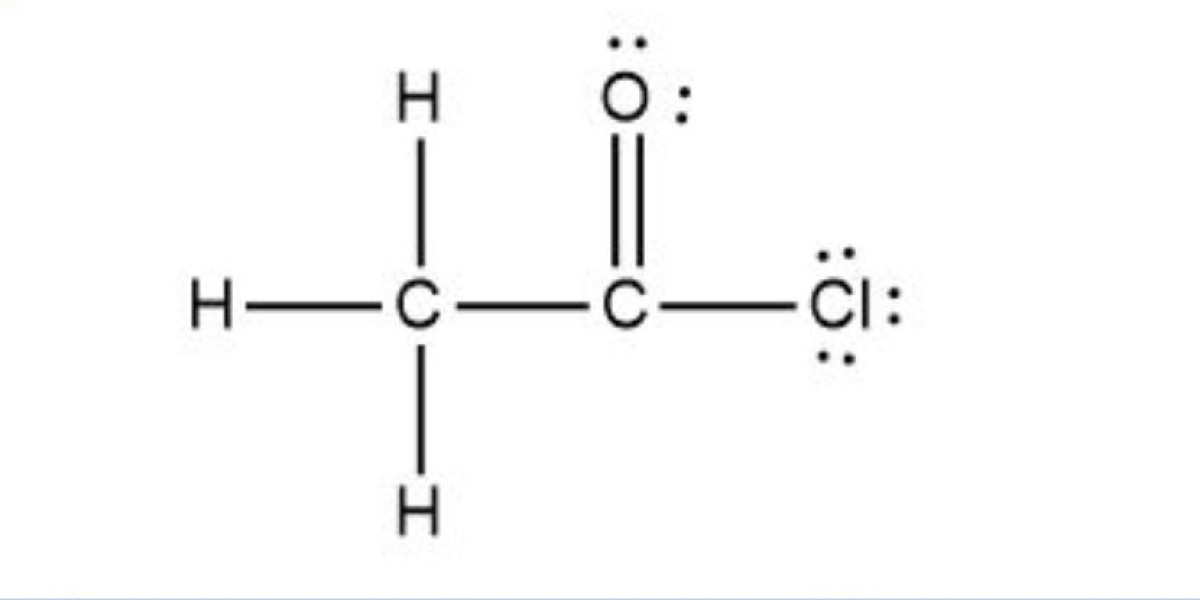
Acetyl chloride is typically produced through the reaction of acetic acid with a chlorinating agent such as thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) or phosphorus trichloride (PCl₃). The production process requires precise control over reaction conditions to ensure the desired purity and yield of the product.
1. Raw Materials
The key raw materials for the production of acetyl chloride include:
- Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH): Acetic acid serves as the source of the acetyl group, which is essential for the production of acetyl chloride.
- Chlorinating Agents: Common chlorinating agents used in acetyl chloride production include thionyl chloride (SOCl₂), phosphorus trichloride (PCl₃), or chlorine gas. Thionyl chloride is the most commonly used reagent due to its favorable reaction kinetics and the byproducts formed.
- Solvents: Organic solvents, such as toluene or chloroform, may be used to facilitate the reaction and assist with the separation of byproducts.
2. Reaction Process
The primary chemical reaction for the production of acetyl chloride is:
CH₃COOH + SOCl₂ → CH₃COCl + SO₂ + HCl
This process involves the following steps:
- Chlorination: Acetic acid is reacted with thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) in a reactor vessel under controlled conditions. The chlorinating agent breaks the C-H bond in acetic acid, replacing the hydroxyl group with a chlorine atom.
- Byproduct Formation: The reaction generates sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) as byproducts. These gases are typically removed from the reaction mixture through condensation and absorption.
- Product Separation: The acetyl chloride (CH₃COCl) is separated from the reaction mixture using distillation, where acetyl chloride is purified to the desired concentration.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
3. Distillation and Purification
After the reaction is completed, the product is separated from the reaction mixture. The acetyl chloride is purified using fractional distillation, which separates the acetyl chloride from other byproducts such as unreacted acetic acid and thionyl chloride.
- Cooling and Condensation: The reaction gases (HCl and SO₂) are typically condensed and absorbed to prevent environmental pollution.
- Distillation: The acetyl chloride is distilled at specific temperatures under reduced pressure to isolate it from the remaining impurities.
4. Packaging and Storage
Once purified, acetyl chloride is cooled and stored in specialized containers made of materials such as glass or steel. Since acetyl chloride is highly reactive and corrosive, it is critical to ensure that all containers are securely sealed and properly labeled. The product should be stored in a cool, dry place to prevent decomposition or reaction with moisture.
Key Considerations for Setting Up an Acetyl Chloride Manufacturing Plant
1. Location and Infrastructure
Choosing the right location is essential for the success of the manufacturing plant. Key considerations include:
- Proximity to Raw Materials: The plant should be strategically located near suppliers of acetic acid and chlorinating agents (such as thionyl chloride) to reduce transportation costs.
- Utility Infrastructure: Acetyl chloride production requires substantial amounts of electricity, water, and specialized equipment. Reliable utility infrastructure is critical for smooth operations.
- Environmental Compliance: Given the hazardous nature of the byproducts and chemicals involved in acetyl chloride production, the plant should be located in an industrial zone where environmental regulations can be adequately managed.
2. Equipment and Technology
The following equipment is essential for the efficient production of acetyl chloride:
- Reactor Vessel: A reaction vessel where acetic acid reacts with the chlorinating agent. This reactor should be resistant to corrosion and able to maintain high pressure and temperature.
- Distillation Column: Used for the separation and purification of acetyl chloride from other byproducts.
- Gas Scrubbers: These are used to neutralize and remove hazardous gases such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) that are produced during the reaction.
- Storage Tanks: Specialized tanks are required for storing acetyl chloride, which should be made of corrosion-resistant materials like glass-lined steel or stainless steel.
- Pumps and Heat Exchangers: For the efficient circulation of fluids and for maintaining temperature control during the distillation and reaction processes.
- Filtration Equipment: For removing any solid impurities from the final product.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Safety
The production of acetyl chloride involves highly reactive and hazardous chemicals. Compliance with local and international regulations is essential to ensure the safety of workers and the surrounding environment:
- Hazardous Materials Handling: The plant must adhere to regulations governing the handling, storage, and transportation of hazardous materials. These include regulations set by agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Safety Measures: The plant should implement stringent safety protocols, including proper ventilation, emergency response plans, and fire suppression systems to handle accidents involving volatile chemicals.
- Waste Management: The byproducts (HCl and SO₂) must be handled and neutralized in compliance with environmental laws to prevent pollution.
- ISO Certification: The plant should comply with ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management.
4. Market Demand and Competition
Acetyl chloride has wide applications in the chemical industry, and demand for it is growing in various sectors. Key factors affecting market demand include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Acetyl chloride is used to produce acetylated derivatives, which are crucial intermediates in the production of various drugs.
- Agrochemicals: It is used in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides.
- Plastics and Polymers: Acetyl chloride is involved in producing acetylated cellulose, which is used in film coatings and plastics.
- Fragrance and Flavor Industry: Acetyl chloride is also used in the synthesis of various flavor and fragrance compounds.
5. Financial Projections and Investment
Setting up an acetyl chloride manufacturing plant requires substantial investment. Financial considerations include:
- Initial Capital Investment: Costs include purchasing land, building infrastructure, acquiring machinery, and ensuring compliance with safety and regulatory standards. The capital investment could range from several hundred thousand dollars to millions of dollars, depending on the scale of the operation.
- Operational Costs: These include raw material procurement (acetic acid and chlorinating agents), labor, maintenance, utilities, and waste management.
- Revenue and Profit Margins: Acetyl chloride is a high-value product with a strong market demand, especially in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical sectors. Profit margins can be significant, especially when economies of scale are achieved.
- Return on Investment (ROI): With proper management and efficient production practices, the ROI can be realized within a few years of operation.
FAQs
1. What is acetyl chloride used for?
Acetyl chloride is primarily used as a reagent in organic synthesis, including the production of acetylated derivatives for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and plastics.
2. How is acetyl chloride produced?
Acetyl chloride is produced by reacting acetic acid with chlorinating agents like thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) or phosphorus trichloride (PCl₃) in a controlled reaction process.
3. What are the major byproducts of acetyl chloride production?
The major byproducts of acetyl chloride production are sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and hydrogen chloride (HCl), which must be neutralized and disposed of according to environmental regulations.
4. What safety measures are required in acetyl chloride production?
The plant must implement strict safety measures, including handling hazardous chemicals carefully, installing proper ventilation, and having emergency response plans in place to manage potential accidents.
5. What is the market outlook for acetyl chloride?
The demand for acetyl chloride is growing in various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and plastics, making it a promising market for new manufacturing facilities.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au