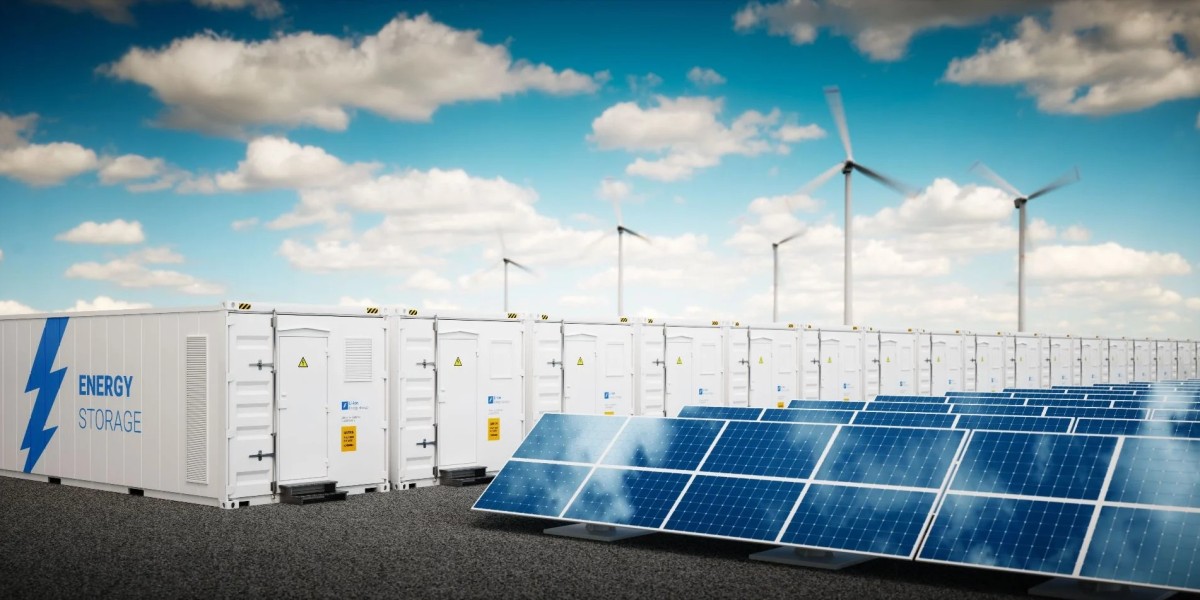
The battery energy storage system (BESS) market has been witnessing significant growth due to its contribution to energy storage solutions, particularly for renewable energy sources. However, despite its promising potential, several factors act as restraints in the expansion of this market. These barriers can hinder the widespread adoption of BESS technologies across various sectors and regions.
High Initial Capital Costs
- One of the primary restraints for BESS adoption is the high upfront cost associated with the installation of battery systems.
- The cost of batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, remains significant, which can limit accessibility for smaller businesses and residential applications.
- While the costs of battery technologies have been declining over the years, they still pose a financial challenge for widespread implementation.
Limited Battery Life and Efficiency
- The lifespan of battery storage systems can be a limiting factor in BESS market growth.
- Batteries degrade over time, losing their efficiency, which necessitates periodic replacement. This creates additional costs for consumers and businesses.
- Reduced efficiency of older battery systems can impact overall system performance, making it less attractive for long-term investments.
Safety and Environmental Concerns
- The safety of BESS technologies, particularly related to the risks of thermal runaway and battery fires, remains a concern.
- There is a potential environmental impact from the disposal of used batteries, especially considering the toxic materials they may contain.
- Regulations on the disposal of lithium-ion batteries and their components are still evolving, and this can cause uncertainty in the market.
Limited Grid Integration
- Integrating BESS technologies with existing energy grids presents technical challenges, particularly for grid stability and reliability.
- In regions where grids are outdated or not fully equipped to handle energy storage, deploying BESS can be more complicated.
- Energy storage systems often face issues with compatibility, and overcoming these integration barriers requires significant investment in upgrading the grid infrastructure.
Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty
- The lack of consistent regulatory frameworks and supportive policies for BESS implementation is a significant restraint in many countries.
- Policy uncertainty can deter investors and companies from committing to large-scale BESS projects.
- While some governments offer incentives and subsidies for renewable energy solutions, these policies are not universally applied, creating a fragmented market.
Technological Limitations
- Despite advancements in battery technology, certain limitations persist, including the energy density of batteries, which affects the overall capacity of storage systems.
- There is ongoing research to improve battery chemistry, but current technologies still have limitations in terms of storage duration and energy efficiency.
- These limitations restrict the ability of BESS to serve as a reliable long-term energy solution for large-scale operations and grid stability.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
- The operational and maintenance costs of BESS systems are often underestimated by consumers and businesses.
- While these systems may lower energy costs over time, the ongoing maintenance, especially for large-scale installations, can accumulate, affecting the overall cost-effectiveness.
- Specialized technical expertise is often required to maintain BESS systems, which adds to operational complexity and cost.
Competition from Alternative Energy Storage Solutions
- BESS faces competition from other energy storage technologies, such as pumped hydro storage, compressed air energy storage, and flywheel energy storage.
- These alternative solutions may be more efficient or cost-effective in certain situations, particularly for large-scale applications.
- As these technologies evolve, BESS may lose market share in some regions or industries, depending on the effectiveness of the alternatives.
Raw Material Supply Chain Issues
- The raw materials required for BESS, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel, are subject to supply chain disruptions.
- Mining and extraction of these materials can be limited by geopolitical factors, trade restrictions, or environmental concerns.
- Supply chain issues can lead to price volatility, which affects the overall cost of battery production and, by extension, the cost of BESS systems.
Public Perception and Market Awareness
- Public awareness about the benefits and potential of BESS remains relatively low in certain regions, which can hinder market adoption.
- Misconceptions about the technology, especially regarding its efficiency and environmental impact, can discourage potential users.
- Increased education and awareness campaigns are needed to build trust in BESS and help consumers and businesses understand its long-term benefits.
Competition from Conventional Energy Systems
- Conventional energy sources like fossil fuels still dominate the global energy market, which creates significant competition for BESS solutions.
- Despite the growing push for sustainability and cleaner energy, transitioning from traditional energy sources to renewable-based storage systems faces resistance due to established infrastructure and vested interests.
- In regions where fossil fuels remain the primary energy source, BESS adoption may be slower due to the entrenched nature of traditional systems.
Battery Supply and Demand Imbalance
- The rapid growth in demand for energy storage systems has led to an imbalance between supply and demand for batteries.
- Manufacturers may face difficulties in scaling production to meet the increasing demand, leading to supply shortages and price increases.
- This imbalance may affect the affordability and availability of BESS technologies, hindering their adoption in new markets.