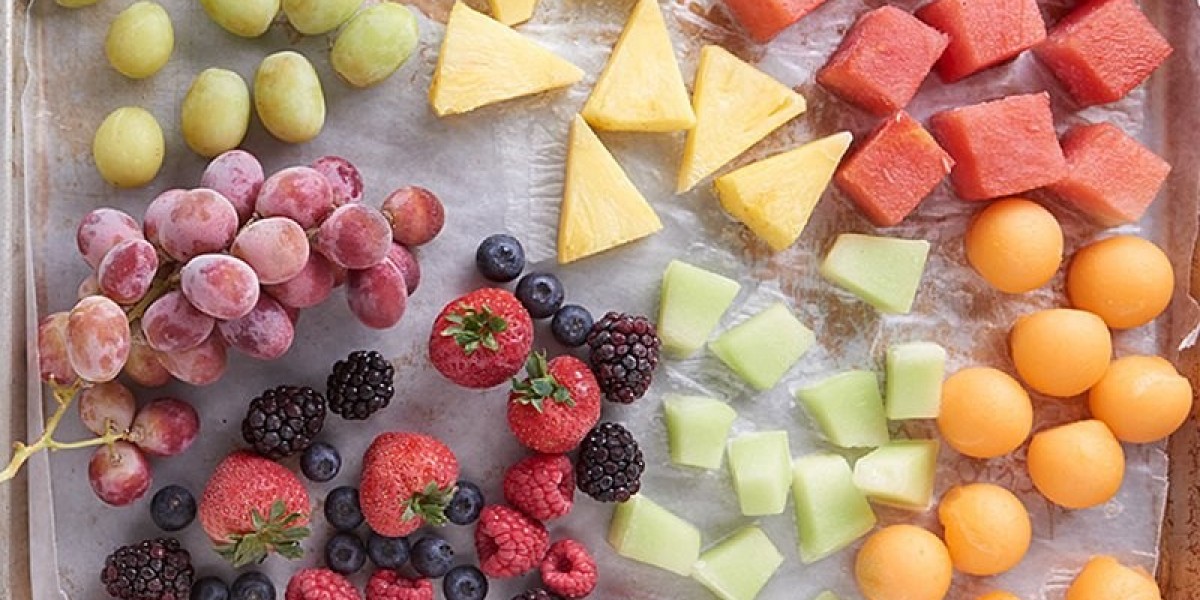
The frozen fruits market is an ever-evolving industry, driven by the increasing demand for healthy, convenient, and affordable food options. With a growing global consumer base, cultural sensitivities are becoming increasingly important to ensure the products cater to local tastes and dietary preferences. From region-specific flavors to ethical considerations, the frozen fruits market must navigate the intricacies of cultural differences to ensure success.
Understanding the Global Landscape
The frozen fruits market has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, driven by changing consumer habits and an increasing preference for convenience. As more people embrace healthy eating and demand products that are easy to store and use, frozen fruits have gained popularity in many parts of the world. However, cultural sensitivities are paramount in the development, packaging, and marketing of frozen fruit products to ensure they resonate with local customs, preferences, and dietary restrictions.
For instance, in Western markets like the U.S. and Europe, frozen fruit blends are often designed to cater to popular smoothie trends, with combinations like mixed berries, mango, and pineapple. Meanwhile, in Asian countries, tropical fruits such as lychee, dragon fruit, and coconut are more widely favored, with frozen products focusing on exotic, vibrant flavors. Thus, understanding the regional preferences and taste profiles is essential for companies operating in the frozen fruits space.
Flavor Preferences Across Regions
One of the most significant cultural sensitivities in the frozen fruits market lies in flavor preferences. What might be popular in one region could be unfamiliar or even unappealing in another. For example, while pineapple and mango are widely consumed in many parts of the world, other fruits like durian or jackfruit, though popular in Southeast Asia, may not have the same appeal in Europe or North America. Therefore, frozen fruit companies must tailor their product offerings based on regional preferences to ensure they meet local demand while maintaining a diverse product range.
Additionally, cultural taboos and dietary restrictions can play a critical role in shaping the frozen fruits market. In some cultures, certain fruits or additives might be avoided for religious, spiritual, or health reasons. For example, in countries with large Muslim populations, ensuring that products are halal-certified is crucial. Similarly, the rise in plant-based and vegan diets worldwide has led to increased demand for dairy-free and non-GMO frozen fruit products. Companies must stay attuned to these trends and offer products that align with the values and needs of their target audience.
Ethical and Sustainable Sourcing: A Cultural Perspective
As consumers across the globe become more conscientious about sustainability and ethical sourcing, the frozen fruits market is increasingly expected to adopt practices that align with these values. In many cultures, environmental responsibility is a key factor in purchasing decisions. Therefore, it is important for companies in the frozen fruits industry to prioritize eco-friendly packaging, fair labor practices, and responsible sourcing of ingredients.
In the European and North American markets, where there is a strong focus on sustainability, frozen fruit brands are increasingly promoting their efforts to reduce food waste and use environmentally friendly packaging. In contrast, in developing countries, the emphasis may be more on supporting local farmers and ensuring that frozen fruit products contribute to the economic well-being of communities.
Adapting Marketing to Cultural Sensitivities
The marketing strategies used to promote frozen fruits must also reflect cultural sensitivities. In some regions, the image of a product might need to be adjusted to appeal to local ideals and values. For instance, marketing messages in Western countries might emphasize health and convenience, while in Asian markets, the focus might be on the natural and exotic aspects of the fruits.
Additionally, colors, packaging design, and language play a significant role in how frozen fruit products are perceived. In certain cultures, colors hold strong symbolic meanings, and understanding these meanings can help brands design packaging that resonates with local consumers. For example, red is often associated with luck and prosperity in many Asian cultures, while in Western markets, it may symbolize excitement or energy.
Conclusion: A Sensitive and Strategic Approach
In the competitive landscape of the frozen fruits market, cultural sensitivities are not just a consideration but a necessity. The key to success lies in understanding and respecting the diverse preferences, dietary restrictions, and values of consumers across the globe. By taking a strategic approach to flavor selection, ethical sourcing, and marketing, companies can tap into the growing demand for frozen fruits while fostering loyalty and trust among diverse consumer bases.