Knee pain can be incredibly debilitating, affecting your daily life and making even the most basic activities a struggle. If you're experiencing knee discomfort that seems persistent and has not improved with home remedies or non-invasive treatments, it may be time to consult with a doctor. Knee replacement surgery is a potential solution that can alleviate pain and restore mobility, enabling you to live a more active and fulfilling life. In this blog, we will explore the procedure, when to opt for surgery, and essential post-surgery instructions. We’ll also provide expert insights from renowned orthopedic specialists, particularly focusing on one of the best orthopedic hospitals in Mumbai.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
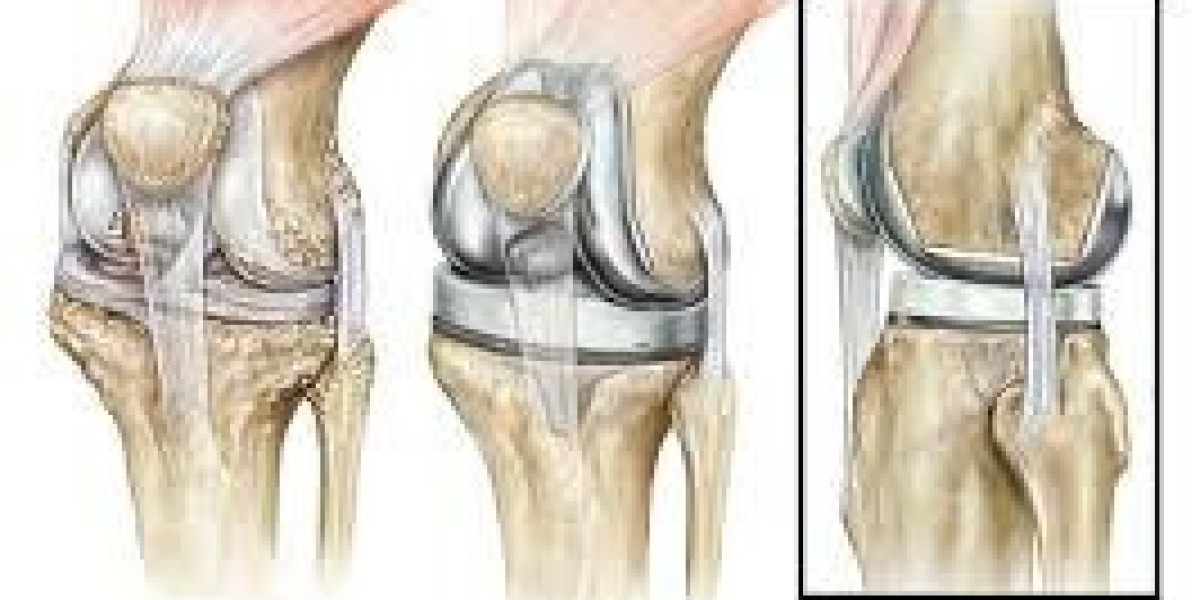
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a procedure designed to replace damaged or diseased parts of the knee with prosthetic components. The damaged area of the knee is removed, and a new artificial joint is put in place. The prosthetic components may be made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials, carefully designed to mimic the movement of a healthy knee joint.
During the surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged bone and cartilage, reshaping the knee joint to accommodate the prosthetic components. The prosthetics are then secured into place, and the joint is realigned for optimal movement. The primary goal of knee replacement surgery is to reduce pain and improve function, enabling patients to perform everyday tasks with greater ease.
When Should You Opt for Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knowing when to consider knee replacement surgery can be a crucial decision for your long-term health. Several factors come into play when determining if surgery is necessary:
- Chronic Knee Pain: If your knee pain has become persistent and significantly interferes with daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or getting in and out of a car, you may want to explore surgical options.
- Failure of Non-Surgical Treatments: Before opting for surgery, doctors typically recommend non-surgical treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or the use of assistive devices like a cane. If these methods fail to provide relief, knee replacement surgery may be considered as the next step.
- Limited Mobility: If you find it difficult to walk, jog lightly, or even stand after sitting for extended periods, this may indicate the need for surgical intervention. A knee that no longer allows you to engage in normal daily activities may require the support of an artificial joint.
- Severe Degeneration: In cases of advanced arthritis or knee injury, the cartilage and bones within the joint may be so worn down that surgery is necessary to improve joint function and alleviate pain.
Conditions That Lead to Knee Replacement Surgery
Several conditions may lead to the need for knee replacement surgery. Some of the most common ones include:
- Osteoarthritis: This condition occurs when the cartilage between the knee bones wears away, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. If conservative treatments such as pain relievers and physical therapy are ineffective, knee replacement surgery might be recommended.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune disorder leads to inflammation and the destruction of the knee joint lining. It can result in significant pain and deformity, often requiring knee replacement surgery as a last resort.
- Knee Deformities: Conditions like bowed legs or knock knees can affect the functionality of the knee joint. These bony deformities can cause pain and may necessitate knee replacement surgery if they are severe enough.
- Previous Knee Injuries: If you've suffered a knee injury, such as a fractured bone or torn ligament, the damage may cause long-term pain and stiffness. When conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, surgery may be the only viable option.
- Chronic Pain and Swelling: In cases where the knee remains swollen and painful despite attempts at non-surgical interventions, a knee replacement can provide significant relief and improve quality of life.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
After a thorough examination, your orthopedic surgeon will determine which type of knee replacement surgery is best suited for your condition. There are several types of knee replacement procedures, including:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Also known as bilateral knee replacement, this procedure involves replacing the entire knee joint, including the damaged cartilage, bone, and ligaments. Total knee replacement is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis or knee damage in both knees. Advances in technology, such as computer-assisted prosthesis alignment, allow for greater precision during surgery.
- Unicondylar (Partial) Knee Replacement: In cases where only one part of the knee joint is severely damaged, a partial knee replacement may be performed. This minimally invasive surgery is less traumatic to the surrounding tissues, resulting in a faster recovery and shorter hospital stay.
- Patellofemoral Knee Replacement: This procedure is performed when the damage is limited to the knee cap (patella). In this case, only the undersurface of the patella is replaced, providing pain relief without the need for a full knee replacement.
- Cartilage Restoration: For patients with isolated cartilage damage, cartilage restoration techniques, such as grafting or using cartilage cells, may be used. This approach aims to repair or regenerate the damaged cartilage, potentially delaying the need for a full knee replacement.
Post-Surgery Care and Instructions
After undergoing knee replacement surgery, following proper rehabilitation and post-surgery care is essential to ensure the best possible outcome. Here are some key instructions to follow after the surgery:
- Avoid Heavy Physical Activity: It's important to avoid strenuous activities such as lifting heavy weights or performing high-impact cardio exercises, as they may place undue stress on the new knee joint.
- Limit Squatting and Kneeling: Squatting or kneeling can place excessive strain on the knee joint, so it's best to avoid these positions to prevent damage to the prosthetic joint.
- Use a Commode: After surgery, using an Indian-style toilet may put unnecessary pressure on the knee joint. Instead, opt for a commode or regular toilet for convenience and comfort.
- Avoid Sitting on the Floor: Sitting on the floor with crossed legs can affect the knee joint's alignment and put stress on the replacement. It's advisable to sit on chairs with appropriate support to maintain proper posture.
- Follow a Rehabilitation Plan: Physical therapy and regular follow-up visits with your orthopedic surgeon will be essential for your recovery. Rehabilitation will help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve mobility.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic knee pain due to arthritis, injury, or other conditions. By understanding the procedure, identifying when to opt for surgery, and adhering to post-surgery care, you can enhance your chances of a successful recovery. Consulting with an experienced orthopedic surgeon at a reputable hospital can guide you through the decision-making process and help you determine the best course of action for your unique needs. Don't let knee pain hold you back from living an active, fulfilling life—explore your options for knee replacement surgery and take the first step toward a more comfortable future.
Follow The Links For Other Related Treatments :-
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/gynecology/cardiotocography-ctg
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/gynecology/bartholins-cyst-treatment
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/gynecology/myomectomy
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/pulmonology
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/pulmonology/bronchoscopy-surgery
https://www.edhacare.com/hospital/max-hospital-new-delhi
https://www.edhacare.com/ny/treatments/gynecology/vaginal-vault-prolapse-surgery
https://www.edhacare.com/hospital/sunshine-hospital-in-hyderabad
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/surgical-oncology/thoracic-surgery
https://www.edhacare.com/pt/treatments/cardiology/cardiac-asthma-treatment