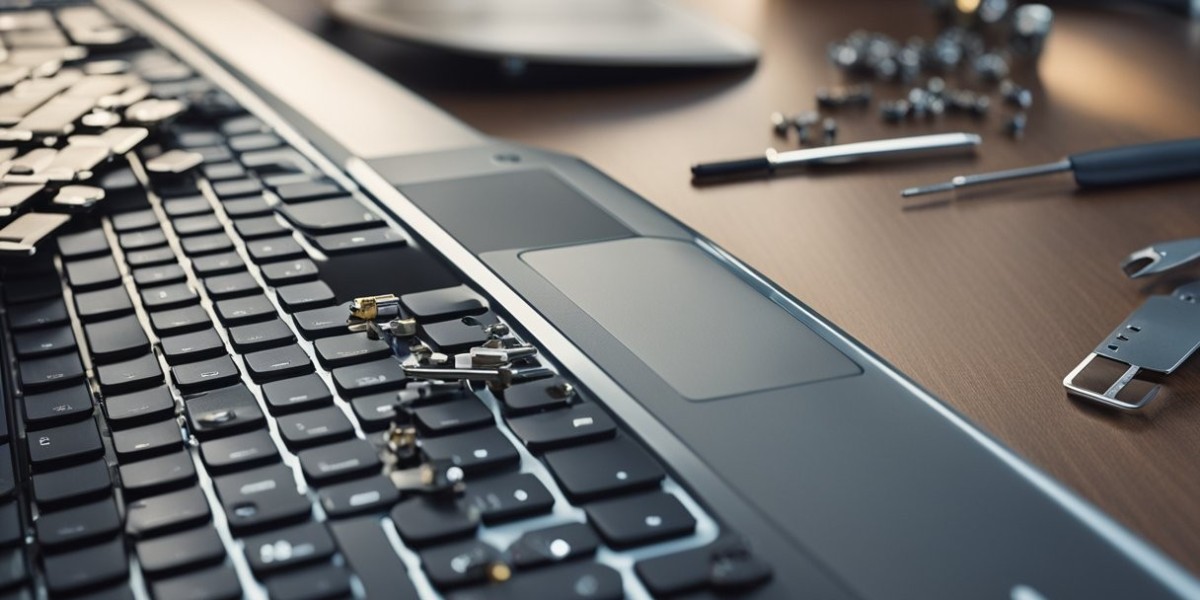
A laptop’s touchpad is an essential component, enabling users to navigate without the need for an external mouse. When this device fails, it can significantly impact productivity and usability. Addressing touchpad issues involves both identifying software glitches and examining physical connections.
Solutions might range from reinstalling drivers to resetting system configurations or even replacing hardware. Early identification and resolution can prevent the hassle of dealing with a non-functional touchpad in critical situations.
Some individuals may prefer to troubleshoot these problems themselves, while others might seek professional repair services. Tools and patience can be the best allies when opting for a DIY approach. Understanding the root cause is crucial when dealing with these common but sometimes tricky issues.
Diagnosing Touchpad Issues
Diagnosing touchpad issues involves determining the root cause, whether it lies in the hardware or software. Common problems need identification, hardware functionality requires checking, and software settings may need adjustments.
Identifying Common Problems
Common touchpad issues often include unresponsiveness, erratic movement, or partial functionality. Users might experience a frozen cursor or jumpy movement, which can hinder productivity. Dust and debris can interfere with the touchpad's responsiveness.
A worn-out touchpad surface can affect input accuracy. Physical damage such as cracks can result in functionality loss. Awareness of these factors can help in pinpointing potential issues quickly.
Checking for necessary driver updates is also crucial, as outdated drivers can lead to touchpad malfunctions. Driver incompatibility may cause inconsistent touchpad behavior.
Conducting a Hardware Test
To start a hardware test, ensure the laptop is powered off. Carefully inspect the touchpad for visible damage or debris. Clean the touchpad surface with a soft, lint-free cloth to remove any dirt or foreign materials.
Check the connection. Loose internal connections can lead to intermittent issues. If accessible, ensure the touchpad cable is securely connected to the motherboard. If the touchpad remains non-functional, consider testing with an external mouse.
During hardware tests, exercise caution to avoid causing further damage. Users with limited technical skills may benefit from professional evaluation to prevent complications.
Software Troubleshooting
Software troubleshooting typically begins with checking the touchpad settings. Navigate to the Control Panel or Settings to verify touchpad functionality is enabled. In some cases, users accidentally disable the touchpad through keyboard shortcuts or settings adjustments.
Updating or reinstalling touchpad drivers can resolve software-related malfunctions. Access the device manager to check the status of installed drivers. Driver rollback might be necessary if a recent update leads to issues.
Another step involves performing a system restore to return settings to a functional state. If unsuccessful, consider operating system updates, as software patches might address compatibility issues affecting the touchpad.
Step-by-Step Repair Guide
Repairing a laptop touchpad involves component replacement, driver reinstallation, and calibration. Each of these steps requires careful attention and the right tools.
Replacing Touchpad Components
To begin, ensure the laptop is turned off and unplugged. Use a screwdriver to remove the screws from the laptop base, then gently open the casing. Locate the touchpad area, often secured with additional screws or adhesive.
Carefully disconnect any cables linking the touchpad to the motherboard. If replacing the touchpad, ensure the new component matches the specifications of the old one. Re-secure the new touchpad, reconnect the cables, and close the casing. This process restores physical functionality, addressing hardware issues like unresponsiveness or erratic cursor movement.
Reinstalling Drivers
Sometimes, the touchpad issues stem from outdated or corrupt drivers. Access the Device Manager by searching for it in the Start Menu. Locate the touchpad under Mice and other pointing devices. Right-click on it and choose Update driver.
Opt for Search automatically to let the system find updates or Browse my computer if you have downloaded them from the manufacturer’s website. This step helps the hardware interface correctly with software. Restart the laptop to apply changes. If issues persist, consider uninstalling the driver and letting the system reinstall it upon reboot.
Calibrating the Touchpad
After ensuring hardware and driver functionality, calibration fine-tunes the touchpad’s sensitivity and accuracy. Go to Settings, select Devices, and navigate to Touchpad. Adjust settings like sensitivity, scroll direction, and gesture configuration based on user preference.
For advanced settings, look for an Additional settings option, leading to the touchpad’s properties window. Utilize presets or calibrate manually based on individual needs. Calibration resolves issues such as poor responsiveness or inconsistent gesture performance. Regular recalibration can maintain performance and enhance user experience.