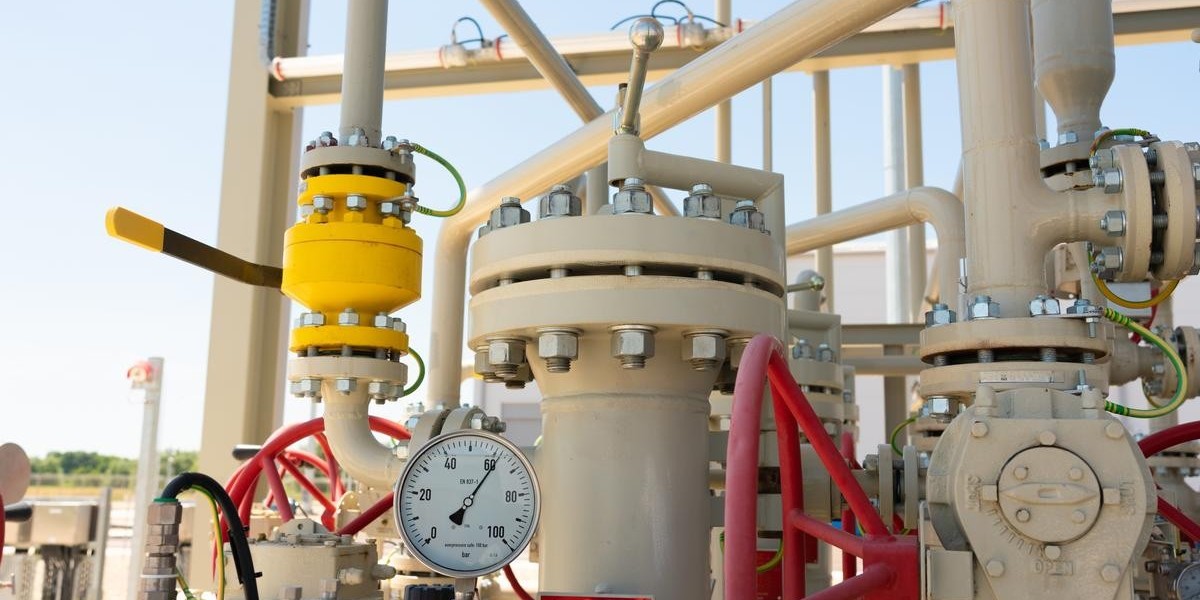
Gas pressure reduction stations play a vital role in the safe and efficient distribution of natural gas across various industries and residential areas. These stations are essential for maintaining consistent pressure levels as gas travels through pipelines, ensuring that end-users receive a steady and reliable supply of this valuable resource. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate operations of gas pressure reduction stations, shedding light on their significance, components, and operational best practices.
Understanding Gas Pressure Reduction Stations
Gas pressure reduction stations, also known as pressure regulating stations, are critical facilities within the natural gas distribution network. Their primary function is to reduce the high pressure of gas transported through pipelines from production sites to distribution points, where the gas is then supplied to consumers. By regulating and lowering the pressure, these stations ensure the safe and controlled flow of gas along the entire distribution network.
Components of Gas Pressure Reduction Stations
A gas pressure reduction station consists of several key components that work collaboratively to achieve efficient pressure reduction and gas distribution:
Inlet and Outlet Piping
The inlet piping connects the high-pressure gas source to the station, while the outlet piping connects the station to the downstream distribution pipelines. Both play a crucial role in facilitating the smooth movement of gas through the station.
Pressure Regulators
Pressure regulators are the heart of the station. These devices control the gas pressure by automatically adjusting the valve openings based on the desired outlet pressure. Modern pressure regulators are equipped with advanced sensors and control systems that ensure precise and consistent pressure regulation.
Safety Systems
Safety is of paramount importance in gas pressure reduction stations. These stations are equipped with various safety systems, including relief valves, emergency shutdown mechanisms, and gas leak detection systems. These systems help prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of both station personnel and the surrounding environment.
Pressure Gauges and Monitoring Equipment
Pressure gauges and monitoring equipment provide real-time data on pressure levels, flow rates, and other essential parameters. This information allows operators to make informed decisions and promptly address any deviations from the optimal operating conditions.
Operational Best Practices for Gas Pressure Reduction Stations
Operating gas pressure reduction stations requires a thorough understanding of the equipment, processes, and safety protocols. Here are some best practices to ensure the effective and safe operation of these critical facilities:
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Scheduled maintenance and regular inspections are essential to keep all components of the station in optimal condition. Any signs of wear and tear or potential issues should be addressed promptly to prevent disruptions in gas distribution.
Personnel Training and Safety Protocols
Station personnel should undergo comprehensive training to handle emergency situations, operate the equipment, and follow safety protocols diligently. This training ensures that they can respond effectively to any unforeseen circumstances and minimize risks.
Monitoring and Data Analysis
Continuous monitoring of pressure, flow rates, and other relevant parameters is crucial for identifying trends and anomalies. Data analysis can provide insights into the station's performance and help optimize its efficiency.
Emergency Preparedness
Gas pressure reduction stations should have well-defined emergency response plans in place. These plans should cover scenarios such as gas leaks, equipment failures, and natural disasters. Regular drills and simulations ensure that personnel are well-prepared to handle emergencies.
The Future of Gas Pressure Reduction Stations
As technology advances, gas pressure reduction stations are expected to become even more sophisticated and efficient. Automation, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance will likely play significant roles in enhancing the operations of these stations. This evolution will contribute to safer gas distribution and a more sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
Gas pressure reduction stations are the unsung heroes of the natural gas distribution network. Their intricate operations and vital role in maintaining safe pressure levels ensure that homes, businesses, and industries receive a consistent and reliable supply of natural gas. By adhering to operational best practices and embracing technological advancements, these stations will continue to pave the way for a seamless and efficient gas distribution system.