Report Overview
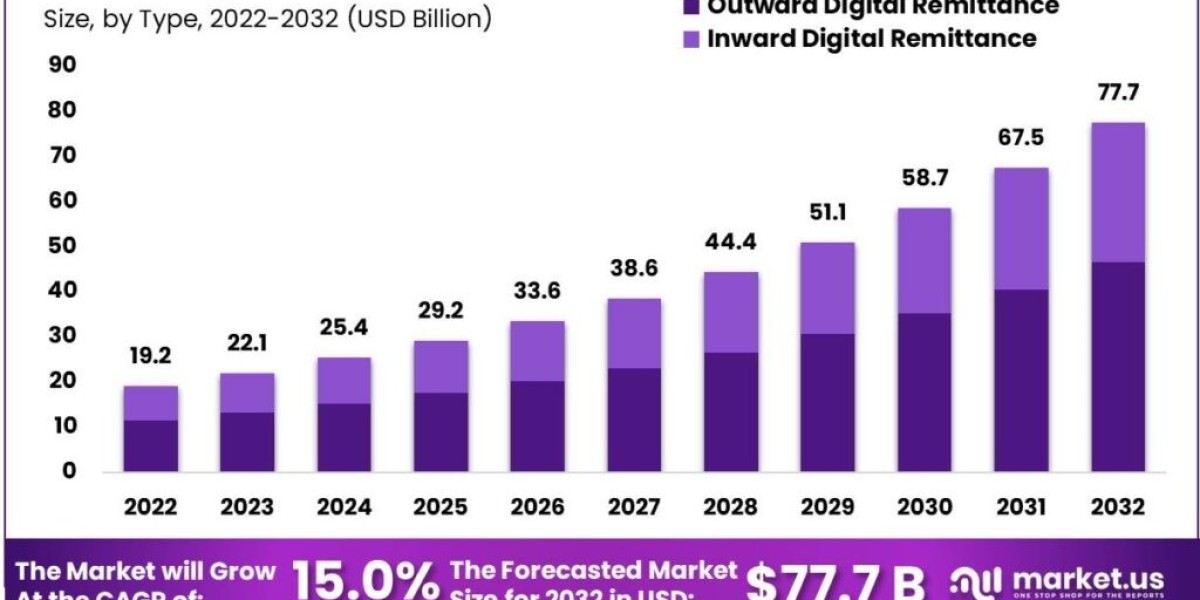
The Global Digital Remittance Market is anticipated to reach a valuation of USD 22.1 Billion in 2023, driven by mobile-based remittance solutions. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for the global market, leading to a projected CAGR of 15.0% between 2023 and 2032. It is estimated to gain a valuation of approximately USD 77.7 Billion by 2032.
What are the regulatory implications of the digital remittance market?
The digital remittance market is rapidly growing and evolving, and regulators around the world are still grappling with the regulatory implications of this new technology.
Some of the key regulatory implications of the digital remittance market include:
- Anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations: Digital remittance providers are subject to AML and KYC regulations, which require them to verify the identity of their customers and to monitor their transactions for suspicious activity. This can be challenging for digital remittance providers, as they often operate across borders and deal with customers from different jurisdictions.
- Consumer protection regulations: Regulators are also concerned about consumer protection issues in the digital remittance market. For example, consumers need to be protected from fraud and from unfair fees and exchange rates.
- Data privacy and security regulations: Digital remittance providers collect a significant amount of data about their customers, including their financial information and personal details. Regulators need to ensure that this data is protected from unauthorized access and use.
- Innovation and competition: Regulators also need to balance the need to protect consumers and prevent financial crime with the need to promote innovation and competition in the digital remittance market.
Here are some specific examples of regulatory initiatives related to the digital remittance market:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an intergovernmental organization that sets standards for combating financial crime, has issued guidance on how AML and KYC regulations should be applied to digital remittance providers.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) in the United States has issued guidance on how consumer protection regulations should be applied to digital remittance providers.
- The European Union has adopted the Payment Services Directive (PSD2), which regulates digital remittance providers and other payment service providers.
- The United Kingdom has adopted the Electronic Money Regulations (EMRs), which regulate digital remittance providers and other electronic money issuers.
These are just a few examples of the regulatory initiatives related to the digital remittance market. As the market continues to grow and evolve, we can expect to see more regulatory activity in this area.
It is important to note that the regulatory landscape for the digital remittance market varies from country to country. Digital remittance providers should consult with legal and regulatory experts to ensure that they are in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.

![[Talk to Live Person] How to Call QuickBooks Payroll Support Phone Number?](https://insta.tel/upload/photos/2024/12/nRJZ6X44UYFnLx6Xzdzc_26_46852e9245af27ffeb16012dee77b7d8_image.jpg)
