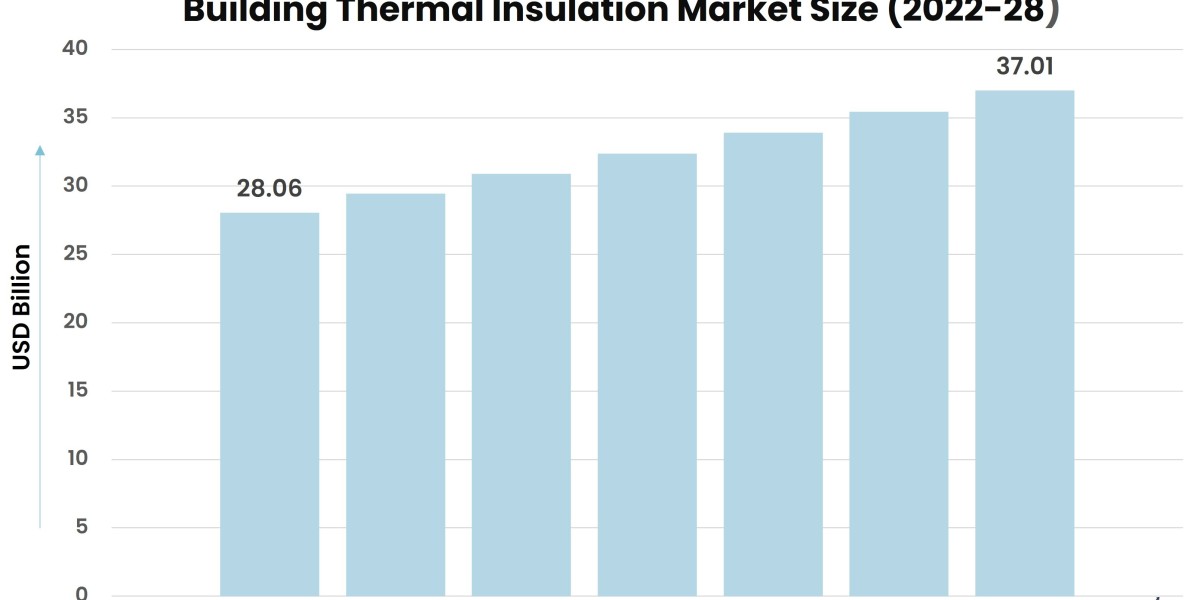
According to Stratview Research, the building thermal insulation market was estimated at USD 28.06 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 4.66% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 37.01 billion in 2028.
In an era defined by rapid urbanization, climate change, and technological advancement, the construction industry is facing unprecedented challenges and opportunities. Central to the evolution of modern building practices is the quest for energy efficiency, sustainability, and occupant comfort. At the forefront of this movement is thermal insulation, a critical component that has seen remarkable innovation and adaptation in recent years. In this article, we explore the latest trends and innovations shaping the future of thermal insulation in construction.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials:
One of the most significant trends in thermal insulation is the growing emphasis on sustainability and the use of eco-friendly materials. With increasing awareness of environmental issues, builders and homeowners alike are seeking insulation solutions that minimize carbon footprint and promote resource conservation. As a result, there has been a surge in demand for insulation materials made from recycled or renewable sources, such as recycled cellulose, sheep's wool, and recycled denim. Additionally, bio-based materials like cork, hemp, and straw are gaining traction for their sustainability credentials and excellent thermal performance.
High-Performance Insulation Technologies:
Advancements in material science and engineering have led to the development of high-performance insulation technologies that offer superior thermal resistance in thinner profiles. Aerogels, for example, are lightweight, nanoporous materials with ultra-low thermal conductivity, making them highly effective at insulating against heat transfer. Vacuum insulated panels (VIPs) utilize a vacuum-sealed core to minimize conductive heat transfer, offering exceptional insulation properties in a compact form factor. These technologies enable builders to achieve higher levels of thermal performance while minimizing space requirements, making them ideal for energy-efficient construction in urban environments with limited footprint.
Innovative Application Techniques:
Alongside material advancements, innovative application techniques are reshaping the way thermal insulation is installed in buildings. Spray foam insulation, for instance, offers unparalleled versatility and adaptability, allowing contractors to insulate complex geometries and hard-to-reach areas with ease. Additionally, prefabricated insulation panels and modular systems streamline the construction process, reducing labor costs and construction time while ensuring consistent insulation performance across the building envelope. These innovative techniques not only enhance efficiency and quality but also enable designers to push the boundaries of architectural creativity.
Integration with Smart Building Technologies:
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to permeate the built environment, thermal insulation is increasingly being integrated with smart building technologies to optimize energy usage and enhance occupant comfort. Smart insulation systems equipped with sensors and actuators can dynamically adjust thermal properties in response to changing environmental conditions, maximizing energy savings and maintaining optimal indoor comfort levels. Furthermore, data-driven analytics provide valuable insights into building performance, enabling predictive maintenance and optimization of energy efficiency strategies over time.
Conclusion:
The future of thermal insulation in construction is characterized by innovation, sustainability, and integration with smart technologies. As the industry continues to evolve, builders, designers, and manufacturers must embrace these trends and capitalize on opportunities to create buildings that are not only energy-efficient and sustainable but also comfortable and resilient in the face of changing environmental conditions. By leveraging cutting-edge materials, techniques, and technologies, we can build a future where thermal insulation plays a central role in shaping the built environment for generations to come.