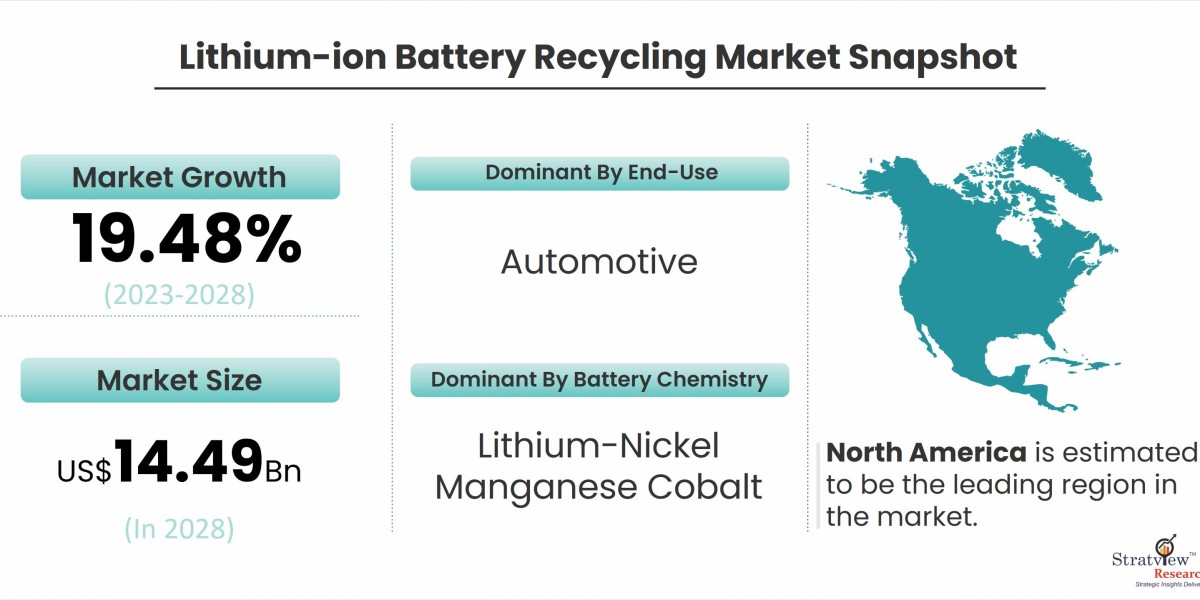
According to Stratview Research, the lithium-ion battery recycling market was estimated at USD 4.96 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 19.48% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 14.49 billion in 2028.
In the pursuit of a sustainable future, industries worldwide are reimagining waste as a valuable resource. Nowhere is this transformation more evident than in the emerging landscape of lithium-ion battery recycling. As the demand for lithium-ion batteries surges, driven by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage systems, the need to address the environmental impact of battery disposal becomes increasingly urgent. In this article, we explore how lithium-ion battery recycling is turning waste into wealth, unlocking economic opportunities while mitigating environmental concerns.
The Rise of Lithium-ion Batteries:
Lithium-ion batteries have become indispensable power sources in our modern lives, powering everything from smartphones to grid-scale energy storage systems. Their lightweight, high energy density, and rechargeable nature make them ideal for a wide range of applications. However, the widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries has led to growing concerns about resource depletion, environmental pollution, and social impacts associated with raw material extraction and battery disposal.
The Imperative of Recycling:
Recycling offers a sustainable solution to the challenges posed by the growing volume of spent lithium-ion batteries. By recovering valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other metals from end-of-life batteries, recycling not only conserves natural resources but also reduces the environmental footprint of battery production and disposal. Moreover, recycling supports the transition towards a circular economy, where materials are reused, remanufactured, and recycled, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency.
Market Dynamics:
The landscape of lithium-ion battery recycling is rapidly evolving, driven by various factors:
Technological Innovations: Advances in recycling technologies, including hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, have enabled more efficient and cost-effective recovery of battery materials. Innovative sorting and separation techniques further enhance the feasibility and scalability of battery recycling operations, paving the way for the commercialization of recycling facilities worldwide.
Regulatory Support: Governments and regulatory agencies are implementing policies and incentives to promote battery recycling and reduce reliance on virgin materials. Extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, tax credits, and subsidies encourage manufacturers to invest in recycling infrastructure and adopt sustainable practices, creating a favorable market environment for battery recycling.
Economic Opportunities: The growing demand for recycled battery materials, driven by the expansion of the electric vehicle market and renewable energy sector, creates lucrative opportunities for battery recyclers and material suppliers. Recycled lithium, cobalt, and nickel offer a cost-effective and environmentally responsible alternative to primary production, attracting investments and driving market growth.
Benefits of Lithium-ion Battery Recycling:
Lithium-ion battery recycling offers a myriad of benefits:
Resource Conservation: Recycling conserves valuable metals and minerals, reducing the need for new resource extraction and minimizing environmental impact.
Energy and Emissions Reduction: Recycling consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to primary production, contributing to climate change mitigation and sustainable development goals.
Supply Chain Resilience: Recycling enhances the resilience of the battery supply chain by diversifying sources of critical materials and reducing dependence on geopolitically sensitive regions for resource extraction.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its immense potential, lithium-ion battery recycling faces challenges such as technological limitations, scale-up barriers, and economic viability. Overcoming these challenges requires collaborative efforts from industry stakeholders, policymakers, and research institutions to drive innovation, streamline regulatory frameworks, and incentivize investment in recycling infrastructure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the emerging landscape of lithium-ion battery recycling presents a compelling opportunity to transform waste into wealth, unlocking economic value while addressing environmental concerns. By embracing recycling technologies and sustainable practices, we can create a more resilient and resource-efficient battery ecosystem, driving the transition towards a circular economy and sustainable future. From waste to wealth, lithium-ion battery recycling exemplifies the transformative power of innovation and collective action in building a greener, more prosperous world.