sudden tooth pain and sensitivity can be alarming, especially when they seem to come out of nowhere. Tooth sensitivity is typically a reaction to specific triggers, such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages. When it occurs suddenly or is accompanied by pain, it may indicate an underlying dental issue. Understanding the causes of sudden tooth pain and sensitivity can help in finding the right treatment and preventing more serious dental problems.
Common Causes of Sudden Tooth Pain and Sensitivity
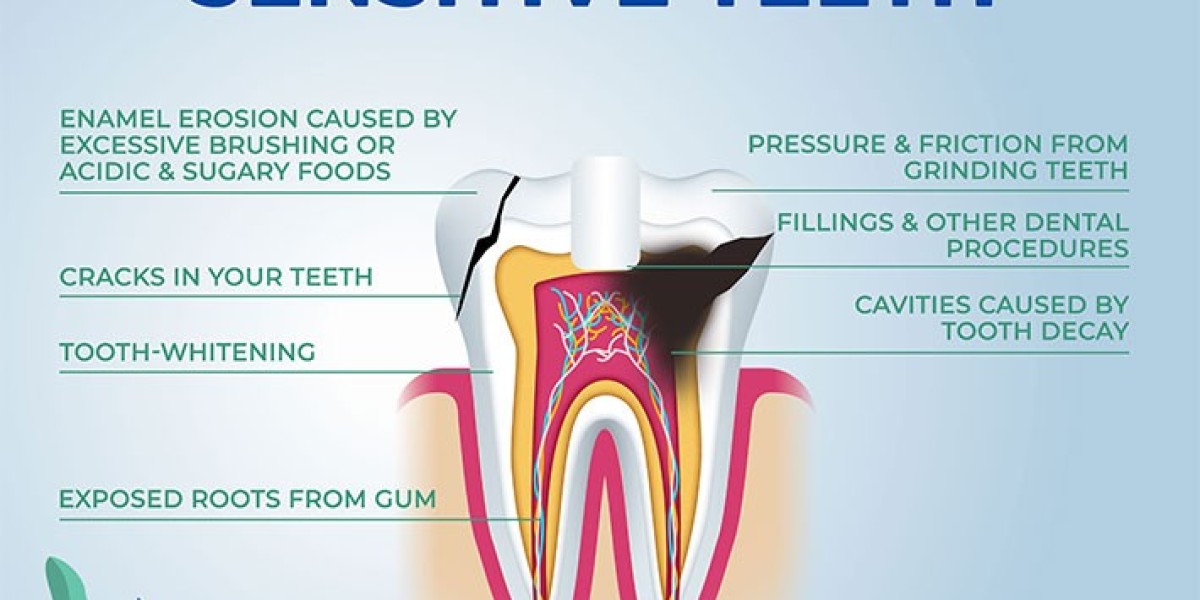
Tooth Decay (Cavities) One of the most common causes of sudden tooth pain is tooth decay. Cavities can form when plaque and bacteria erode the tooth enamel, eventually reaching the dentin and nerve. This can cause sharp pain or sensitivity when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sugary substances.
- Signs: Pain when biting or chewing, visible holes or pits in teeth, and increased sensitivity to sweet foods.
Cracked or Chipped Teeth A crack or chip in your tooth can expose the dentin or even the nerve inside the tooth, leading to sudden pain or sensitivity. You may feel discomfort when chewing, especially if the tooth is fractured, or when exposed to cold air or liquids.
- Signs: Sudden sharp pain, discomfort when chewing, sensitivity to temperature changes.
Gum Recession Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the tooth, exposing the tooth’s root. Since the root lacks the protective enamel layer, it becomes more sensitive to hot, cold, and acidic foods, often leading to sudden sensitivity.
- Signs: Teeth appearing longer than usual, increased sensitivity near the gumline, and swollen or receding gums.
Enamel Erosion Enamel is the outer protective layer of your teeth. Over time, acidic foods and drinks, aggressive brushing, and grinding your teeth can wear down enamel, exposing the sensitive dentin underneath. This can lead to sudden sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods.
- Signs: Dull ache or sharp pain when eating or drinking, visible signs of worn enamel.
Sinus Infection In some cases, a sinus infection can cause tooth pain. The upper teeth, especially the molars, are located near the sinuses, and pressure from a sinus infection can lead to pain that feels like it originates from the teeth.
- Signs: Pain in multiple upper teeth, sinus pressure, congestion, and facial tenderness.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism) Grinding your teeth at night or during periods of stress can wear down enamel and cause sudden sensitivity. Over time, bruxism can also lead to cracks or fractures in the teeth, increasing pain and sensitivity.
- Signs: Jaw pain, headaches, tooth sensitivity in the morning, and flat or worn teeth.
Recent Dental Procedures Tooth pain or sensitivity can develop after dental work such as fillings, crowns, or teeth whitening. This is usually temporary and should resolve within a few days, but it can cause sudden discomfort.
- Signs: Sensitivity to hot or cold following dental treatments, lingering pain after dental procedures.
Abscessed Tooth An abscess is a pocket of infection that forms in the tooth or gums due to untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or trauma. This infection can cause intense, sudden pain, and sensitivity, often accompanied by swelling and fever.
- Signs: Severe toothache, swelling in the gums, fever, and a bad taste in the mouth.
Treatment Options for Sudden Tooth Pain and Sensitivity
Desensitizing Toothpaste Desensitizing toothpaste can help block the sensations from reaching the nerve by covering the exposed dentin. Regular use can reduce sensitivity over time.
- How it helps: Provides relief by blocking pain signals to the tooth nerve.
Fluoride Treatments Professional fluoride applications can strengthen tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay and sensitivity. Over-the-counter fluoride rinses can also help with mild sensitivity.
- How it helps: Strengthens enamel and reduces exposure to temperature changes.
Dental Fillings or Crowns If a cavity, crack, or chip is causing sudden pain, your dentist may recommend a filling, crown, or bonding to restore the tooth and protect the sensitive areas.
- How it helps: Restores the tooth's structure and protects it from further damage.
Gum Grafting For cases of gum recession, a gum grafting procedure can cover the exposed tooth roots, reducing sensitivity and protecting the tooth from further damage.
- How it helps: Covers exposed roots, reducing sensitivity and preventing further gum recession.
Root Canal Therapy If the tooth's nerve is affected by decay or infection, a root canal may be necessary. This procedure removes the infected tissue, alleviating pain and preventing further damage.
- How it helps: Removes the source of the pain by eliminating the infected or damaged nerve tissue.
Sinus Treatment If sinus pressure is causing tooth pain, treating the sinus infection with decongestants or antibiotics can alleviate the discomfort.
- How it helps: Reduces sinus pressure and the associated tooth pain.
Preventing Sudden Tooth Pain and Sensitivity
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and regular dental check-ups can help prevent decay, gum disease, and sensitivity.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: A softer brush is gentler on enamel and gums, reducing the risk of gum recession and enamel wear.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Limiting consumption of acidic beverages like soda, wine, and citrus can help protect enamel from erosion.
- Wear a Mouthguard: If you grind your teeth at night, using a nightguard can protect your teeth from wear and prevent cracks and sensitivity.
- See Your Dentist Regularly: Routine dental visits help catch potential problems early and prevent more serious issues like abscesses and severe tooth decay.
When to See a Dentist
If you experience sudden tooth pain and sensitivity that persists for more than a few days, or if it's accompanied by swelling, fever, or severe pain, it's important to seek professional dental care. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more significant dental issues, including infections, abscesses, or tooth loss.
Conclusion
Sudden tooth pain and sensitivity can have various causes, from cavities and enamel erosion to gum recession and cracked teeth. Fortunately, most cases can be treated effectively with proper dental care. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding abrasive habits, and addressing any signs of dental damage early can help protect your teeth and keep pain at bay. If you’re unsure of the cause of your discomfort, consulting with a dentist will help pinpoint the problem and provide relief.