Introduction
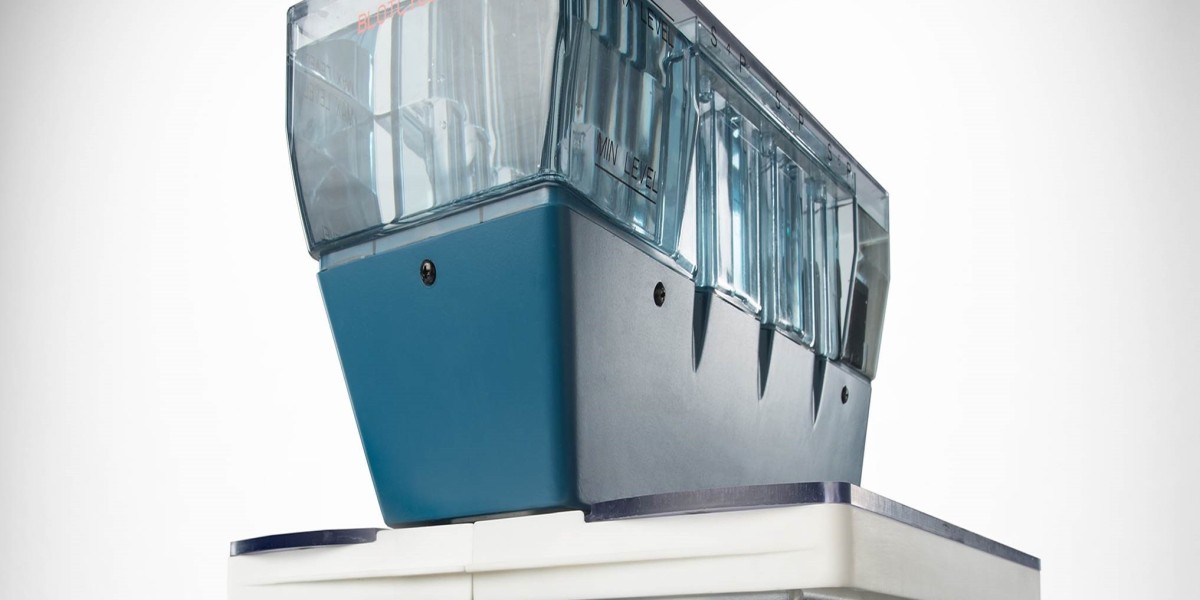
Western blotting, a technique used for detecting specific proteins in a sample, has been a crucial method in molecular biology for decades. It is widely used in research and diagnostics to study protein expression, post-translational modifications, and interactions in various biological systems. The Western Blotting Processors Market, driven by the demand for automated systems that streamline this process, has evolved over the years to meet the growing needs of high-throughput research, diagnostic accuracy, and precision medicine. The impact of these systems on the research and diagnostics sectors is profound, as they shape the future of biotechnology by advancing protein analysis, accelerating discoveries, and enabling better patient outcomes. In this article, we explore how Western blotting processors are influencing research and diagnostics, transforming biotech industries, and paving the way for the next generation of scientific breakthroughs.
The Role of Western Blotting Processors in Research Advancements
1. Accelerating Scientific Discovery
Western blotting processors have revolutionized the pace of scientific discovery by automating a traditionally labor-intensive process. By automating the steps involved in protein separation, transfer, and detection, these systems have enabled researchers to handle higher sample volumes, improve reproducibility, and reduce the time required to obtain reliable results. Automation also minimizes human error, ensuring that data is consistent and reproducible.
High-Throughput Research: Automated Western blotting systems can process large batches of samples simultaneously, making them ideal for high-throughput screening in drug discovery and molecular biology research. With higher throughput capabilities, researchers can perform more experiments in less time, accelerating the discovery of new biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and drug candidates.
Expanded Applications in Proteomics: Western blotting processors are playing an integral role in proteomics, where understanding the entire protein content of a cell or organism is critical. Researchers use Western blotting to investigate protein expression profiles, quantify protein biomarkers, and analyze post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation. As proteomics continues to grow as a field, automated Western blotting systems equipped with high-sensitivity detection technologies have become indispensable tools for exploring complex biological systems.
2. Enabling Drug Discovery and Biopharmaceutical Development
The biotechnology industry has benefited immensely from the integration of Western blotting processors into drug discovery and biopharmaceutical development workflows. Protein analysis is essential for the identification of therapeutic targets, drug efficacy testing, and quality control during the development of biologics and monoclonal antibodies.
Target Validation and Screening: In drug discovery, validating potential therapeutic targets is one of the first steps in developing new drugs. Western blotting is used to assess the expression and activity of proteins of interest, providing critical insights into the mechanisms of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and autoimmune disorders. Automated systems have allowed researchers to conduct these analyses on a much larger scale, with greater sensitivity and accuracy.
Biologics Development: The rise of biologics therapies derived from living organisms, such as monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and gene therapies has further driven the demand for Western blotting processors. These systems are critical for monitoring the production, quality, and stability of biologics, ensuring that these therapies meet stringent regulatory standards. Western blotting processors can detect impurities or changes in protein folding that might compromise the therapeutic potential of biologics.
The Role of Western Blotting Processors in Diagnostics
1. Precision Diagnostics in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has seen significant advancements in diagnostics, with Western blotting processors playing a pivotal role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Western blotting is often used in clinical laboratories to confirm diagnoses, monitor disease progression, and assess therapeutic efficacy, particularly for conditions where protein markers play a critical role in the diagnosis and management of diseases.
Diagnostic Applications in Infectious Diseases: Western blotting is widely used to diagnose a variety of infectious diseases, including HIV, Lyme disease, and hepatitis. For instance, in HIV diagnostics, Western blotting is used to confirm the presence of antibodies to HIV proteins, making it an essential confirmatory test after initial screening. The ability of automated Western blotting systems to process large numbers of patient samples with consistent accuracy is crucial for clinical labs handling high volumes of diagnostic tests.
Cancer Diagnostics and Biomarker Identification: In cancer diagnostics, Western blotting is used to detect specific protein biomarkers that are indicative of tumor presence or progression. For example, detecting the overexpression of certain proteins can help in identifying cancer types or monitoring response to therapy. Automated Western blotting processors equipped with sensitive detection technologies are now able to identify these biomarkers with greater precision, facilitating earlier detection and personalized treatment plans.
2. Point-of-Care Diagnostics
The shift toward point-of-care (POC) diagnostics where medical testing is done outside of centralized laboratories is an emerging trend in healthcare. Miniaturized and portable Western blotting processors are now being developed to address this need, allowing for faster diagnostic results in remote or underserved locations.
Portable Systems for On-Site Testing: Miniaturized Western blotting systems that can be used at the point of care are particularly valuable in emergency situations or areas with limited access to diagnostic infrastructure. For instance, in rural or resource-limited settings, having access to rapid, on-site protein analysis tools can make a significant difference in diagnosing and treating diseases such as infectious diseases, cancers, and autoimmune disorders.
Expanding Global Access to Diagnostics: By offering portable and affordable solutions, the miniaturization of Western blotting processors is helping to expand access to high-quality diagnostics worldwide. These systems are critical for global health initiatives that aim to improve early detection and treatment, especially in low-resource environments.
How Western Blotting Processors Are Shaping the Future of Biotech
1. Advancing Personalized Medicine
Personalized or precision medicine is a growing field that tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, including their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Western blotting processors are playing a crucial role in this shift by enabling the analysis of patient-specific protein markers that can inform diagnosis, treatment plans, and monitoring.
Tailored Therapeutic Approaches: In personalized medicine, understanding protein expression profiles is essential for developing targeted therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Western blotting processors, especially those equipped with high-throughput and high-sensitivity capabilities, enable healthcare providers to assess the protein levels of specific biomarkers in patient samples. This allows for more accurate diagnosis and treatment decisions based on individual protein profiles.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: Western blotting is also used to monitor how well a patient is responding to treatment, particularly in oncology and autoimmune diseases. The ability to measure changes in protein expression levels over time can help clinicians adjust therapies for optimal outcomes, making Western blotting an integral tool in the evolving landscape of personalized medicine.
2. Shaping the Future of Biotech Research and Development
Western blotting processors are not just enhancing existing research and diagnostic capabilities; they are also paving the way for the next generation of biotech innovations. As technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and multiplexed detection continue to advance, Western blotting systems will become even more powerful tools for biotechnology research.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze complex Western blotting data more accurately and efficiently. By training these systems on large datasets, researchers can improve the accuracy of protein quantification and detection, even in challenging biological samples. The integration of AI with Western blotting systems promises to increase both the sensitivity and scalability of protein analysis, facilitating breakthroughs in drug discovery and diagnostics.
Next-Generation Protein Analysis: As biotech companies explore more complex applications such as proteomics, biomarker discovery, and regenerative medicine, the demand for advanced protein analysis tools like Western blotting processors will only grow. These processors will continue to evolve to meet the needs of researchers and clinicians who require more precise, faster, and high-throughput solutions.
Conclusion
Western blotting processors have made a profound impact on both the research and diagnostics sectors, driving advancements in drug discovery, clinical diagnostics, and personalized medicine. Through automation, miniaturization, and technological advancements in detection and data analysis, these systems are enabling faster, more accurate, and more reproducible protein analysis. As the biotechnology industry continues to evolve, Western blotting processors will play a central role in shaping the future of medical research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development. With ongoing innovations in machine learning, AI, and multiplexed detection, the potential for Western blotting to accelerate scientific breakthroughs and improve patient outcomes is immense, positioning it as an essential tool for the next generation of biotech research and healthcare solutions.