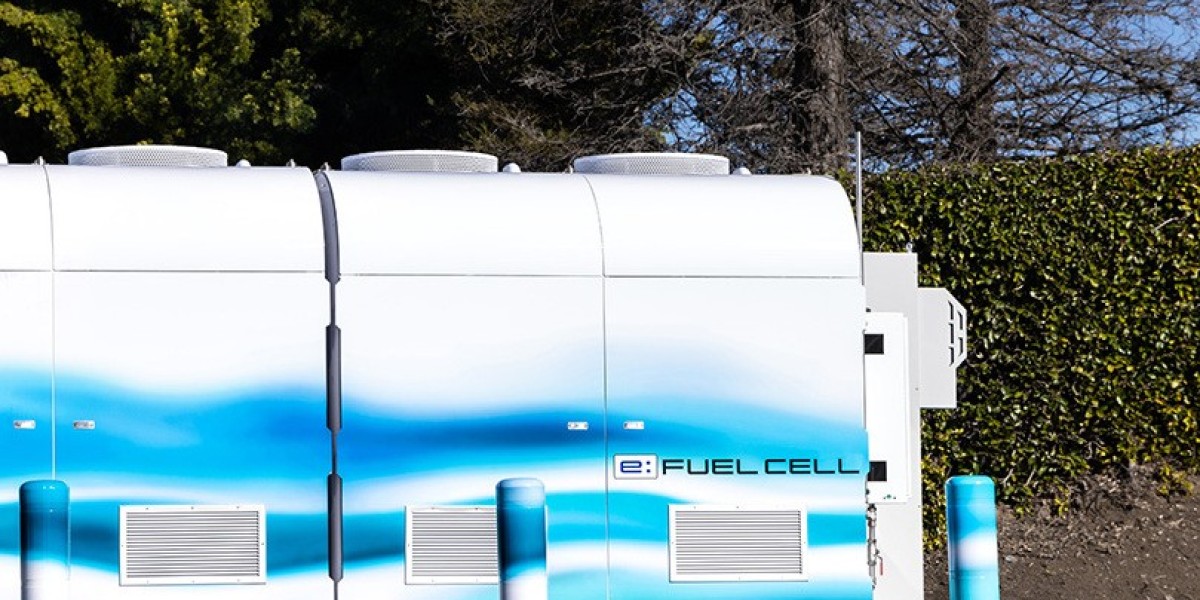
The stationary fuel cell systems market has emerged as a pivotal player in the renewable energy industry, driven by the increasing global demand for sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly power solutions. As traditional energy sources like fossil fuels come under increasing scrutiny for their environmental impact, fuel cell technology presents a viable alternative. Stationary fuel cells, which generate electricity for stationary applications such as residential, commercial, and industrial use, are gaining traction as key components in the transition toward a low-carbon economy.
This market is poised for significant growth due to a variety of factors, including advancements in fuel cell technology, growing environmental concerns, and favorable government policies supporting clean energy initiatives. As the global shift towards decarbonization continues, fuel cells are being seen as a crucial part of the energy mix. Fuel cells offer several benefits over traditional combustion-based power generation, including higher efficiency, lower emissions, and the ability to generate power from renewable resources like hydrogen.
The adoption of stationary fuel cell systems is particularly noticeable in regions with high energy consumption and stringent environmental regulations. In these areas, industries are increasingly opting for fuel cells to reduce their carbon footprint and meet sustainability targets. The ability to scale fuel cell systems to meet the specific power needs of various sectors, from small residential units to large industrial applications, makes them an attractive option for businesses looking to secure a reliable and clean energy supply.
The transition toward hydrogen as a primary fuel source for fuel cells has further fueled market optimism. Hydrogen, when used in fuel cells, produces only water vapor as a byproduct, making it one of the cleanest energy sources available. This is especially significant in the context of growing concerns about air pollution and climate change, with many governments around the world implementing strict emission standards. As a result, the stationary fuel cell market is closely tied to the development of hydrogen infrastructure, which includes the production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen fuel.
In addition to environmental factors, the stationary fuel cell systems market benefits from innovations in technology and manufacturing processes. Continuous research and development in fuel cell efficiency and cost reduction have made fuel cells more commercially viable for both consumers and industries. As the cost of producing fuel cells continues to fall, their adoption becomes more accessible, particularly in regions with supportive infrastructure for renewable energy technologies.
Despite the promising outlook, the stationary fuel cell market faces several challenges that could hinder its full potential. The high initial capital costs associated with fuel cell systems, although decreasing, remain a barrier for widespread adoption. Moreover, the infrastructure for hydrogen production and distribution remains underdeveloped in many parts of the world, which limits the availability of hydrogen fuel and further increases costs. Overcoming these obstacles will require continued investment and collaboration between governments, private companies, and research institutions.
Market players are responding to these challenges by expanding their product offerings and forming strategic partnerships to drive the development of hydrogen infrastructure. Many companies are investing in scaling up their manufacturing capabilities and exploring new applications for stationary fuel cell systems, such as microgrids, backup power solutions, and remote area power generation. In parallel, governments are rolling out policies and incentives to promote the adoption of clean energy technologies, including fuel cells, through tax credits, grants, and subsidies.