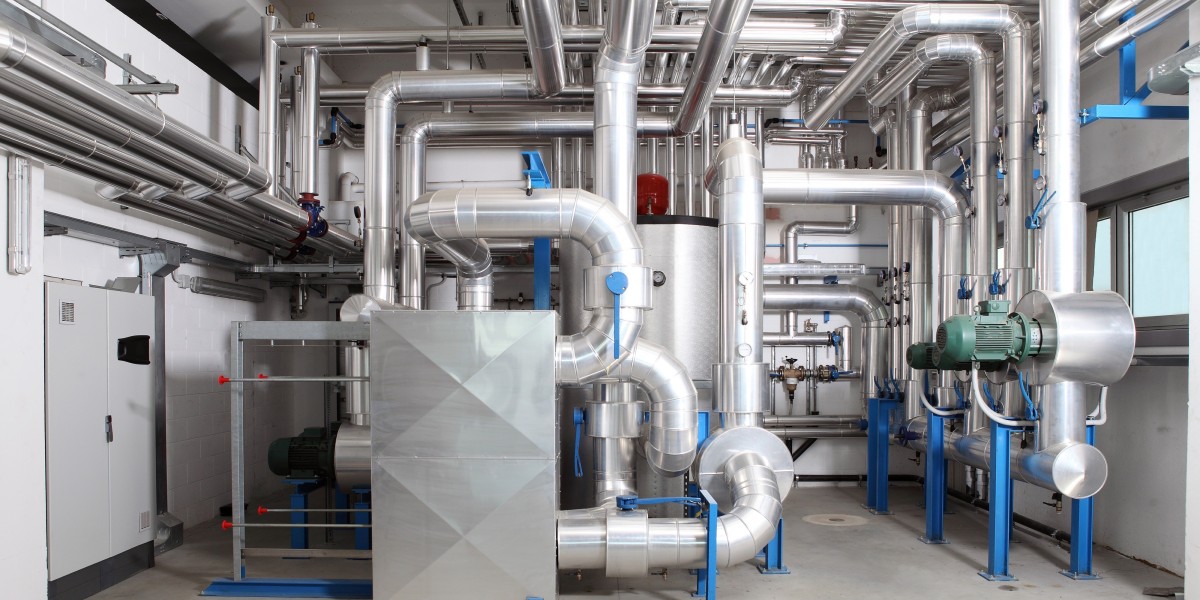
The industrial heat pump market is rapidly gaining momentum as industries look for energy-efficient, sustainable solutions to manage their heating and cooling needs. In particular, heavy industry and process heating sectors are seeing increasing adoption of industrial heat pump technology, driven by the need to reduce energy consumption, minimize operational costs, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. Industrial heat pumps, which transfer heat from one medium to another rather than generating it, provide a compelling alternative to traditional heating systems, offering significant advantages in both efficiency and sustainability.
Industrial applications require reliable and consistent heating, often at high temperatures, for processes such as drying, chemical reactions, metal treatment, and more. In these sectors, energy costs are a major concern, making the adoption of technologies that enhance energy efficiency a strategic priority. Industrial heat pumps are increasingly seen as a viable solution, offering higher efficiency, lower carbon emissions, and the flexibility to integrate with renewable energy sources.
Market Trends: Shaping the Future of Industrial Heat Pumps in Heavy Industry
The industrial heat pump market is experiencing several key trends that are shaping its growth and adoption in heavy industry and process heating applications. These trends reflect a broader shift toward energy efficiency, sustainability, and the need for lower carbon footprints across industrial operations.
1. Energy Efficiency as a Core Driver:
One of the most significant market trends is the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency in industrial operations. As global energy costs rise and industries face mounting pressure to reduce operational costs, the need for systems that provide more efficient heating and cooling has become more urgent. Industrial heat pumps offer a highly energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating technologies like boilers and furnaces.
Heat pumps operate by transferring heat rather than generating it, meaning they require less energy to produce the same amount of heating. In sectors like steel production, cement manufacturing, and petrochemicals, where heat is required continuously and often at high temperatures, heat pumps can reduce energy consumption significantly. These systems can also integrate heat recovery solutions, capturing waste heat from industrial processes and redirecting it to meet heating needs elsewhere in the facility. This closed-loop energy system increases overall efficiency and reduces dependence on external energy sources.
2. Rising Regulatory Pressure for Sustainability:
With governments and regulatory bodies around the world tightening emissions standards, industrial operations are under increasing pressure to adopt low-carbon technologies. Many industrial sectors are subject to carbon taxes, cap-and-trade systems, or increasingly stringent emissions regulations. In response, businesses are prioritizing technologies that help reduce their environmental footprint. Industrial heat pumps are particularly appealing due to their ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil-fuel-powered heating methods.
3. Integration with Waste Heat Recovery:
A growing trend in the industrial sector is the use of waste heat recovery systems, which capture and reuse heat generated by industrial processes that would otherwise be lost. Industrial heat pumps are highly compatible with waste heat recovery, as they can be used to capture excess heat from operations like power generation, metal smelting, or refrigeration, and transfer it to where it is needed in the process. By using heat pumps in conjunction with waste heat recovery, industries can lower their overall energy consumption, enhance operational efficiency, and reduce environmental impact.
4. Advancements in High-Temperature Heat Pump Technology:
A significant barrier to the widespread adoption of industrial heat pumps in heavy industry and process heating has been the ability to achieve high temperatures, as many industrial processes require temperatures well above those typically provided by conventional heat pump systems. However, recent advancements in high-temperature heat pump technology are enabling industrial heat pumps to operate at much higher temperatures than previously possible. These innovations are opening up new opportunities for heat pumps in industries that require high temperature heating, such as metallurgical processing, cement production, and chemical synthesis.
High temperature heat pumps can now provide the necessary thermal output for industrial heating processes, while maintaining the energy efficiency and sustainability benefits that characterize heat pump systems. This breakthrough is expanding the potential applications of industrial heat pumps in heavy industry and making them a more viable alternative to traditional high-temperature heating solutions.
Applications in Heavy Industry and Process Heating
Industrial heat pumps are finding applications across a range of heavy industry and process heating operations, offering significant opportunities for energy savings, improved operational efficiency, and reduced environmental impact.
1. Chemical and Petrochemical Industries:
The chemical industry relies on continuous and often high-temperature heat for processes such as distillation, drying, and chemical reactions. Industrial heat pumps offer an efficient way to meet these demands while lowering energy consumption. By integrating heat pumps into existing systems, chemical plants can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, capture and reuse waste heat, and optimize energy use across their operations.
2. Metal Processing and Manufacturing:
The metal processing sector, which includes industries such as steel, aluminum, and foundries, is one of the highest consumers of energy due to the need for high-temperature heating during smelting, forging, and other metalworking processes. Industrial heat pumps can recover waste heat from metal processing operations and use it for other heating purposes, such as preheating combustion air or providing heating to administrative areas. These systems can also assist in maintaining uniform temperatures across the facility, ensuring more stable production processes.
3. Food and Beverage Industry:
In food processing, where energy-intensive operations such as pasteurization, sterilization, and drying are common, industrial heat pumps can help reduce energy costs while maintaining product quality and safety. For example, waste heat from the pasteurization process can be captured and used to heat water for other parts of the operation, such as cleaning and washing. By using heat pump systems, food manufacturers can achieve significant energy savings while lowering their carbon footprint.