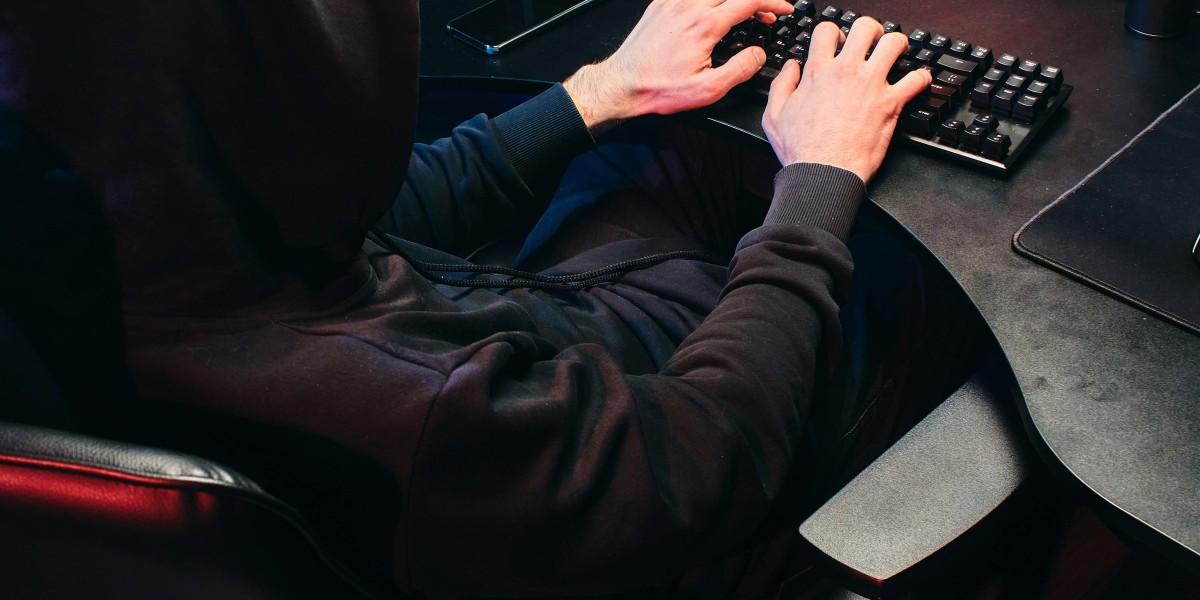
Cybercrime has become an increasingly pressing concern for businesses of all sizes. With the rapid digitalisation of business operations, companies in Sri Lanka and worldwide are facing unprecedented challenges in protecting their digital assets. Many corporate lawyers in Sri Lanka are reporting a surge in cybercrime-related cases, highlighting the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures. The global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making it imperative for businesses to take decisive action in protecting their digital infrastructure.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Cybercrime comes in many forms, from data breaches and ransomware attacks to phishing scams and intellectual property theft. The cost of these attacks extends beyond immediate financial losses, potentially causing long-term damage to reputation, customer trust, and business operations. As business lawyers in Sri Lanka frequently emphasise, the legal implications of data breaches can be severe, potentially resulting in hefty fines and legal liability.
Common Types of Cyber Threats
- Ransomware Attacks: Malicious software that encrypts company data and demands payment for decryption.
- Phishing Scams: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by posing as trustworthy entities.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting communications between two parties.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming systems with traffic to cause service disruption.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating people into divulging confidential information.
Essential Protection Measures for Your Business
- Implement Strong Security Policies
- Policy Development
- Create comprehensive written security policies
- Define clear roles and responsibilities
- Establish security standards for different types of data
- Develop acceptable use policies for company resources
- Implementation guidelines for security measures
- Regular Reviews and Updates
- Quarterly policy assessments
- Annual comprehensive reviews
- Update policies based on new threats
- Incorporate employee feedback
- Align with industry best practices
- Employee Training and Awareness
- Comprehensive Training Program
One of the most vulnerable aspects of any organisation's security is its human element. Regular training sessions should cover:
- Recognition of sophisticated phishing attempts
- Safe password practices and management
- Social engineering awareness and prevention
- Proper data handling procedures
- Incident reporting protocols
- Mobile device security
- Remote work security practices
- Practical Implementation
- Monthly security awareness newsletters
- Quarterly training sessions
- Simulated phishing exercises
- Security awareness games and competitions
- Recognition programs for security-conscious employees
- Technical Security Measures
- Infrastructure Security
- Implementation of next-generation firewalls
- Regular system updates and security patches
- Advanced anti-virus and anti-malware protection
- Network segmentation and monitoring
- Encrypted communications protocols
- Zero-trust security architecture
- Cloud security measures
- Access Control Methods
- Multi-factor authentication implementation
- Biometric verification where appropriate
- Role-based access control systems
- Regular access reviews and audits
- Strong password policies with regular updates
- Secure remote access solutions
- Privileged access management
- Data Protection and Backup
- Leading law firms in Sri Lanka recommend implementing:
- Backup Strategies
- Daily incremental backups
- Weekly full system backups
- Off-site backup storage
- Cloud-based backup solutions
- Regular backup testing and verification
- Disaster recovery planning
- Data Protection Measures
- End-to-end encryption for sensitive data
- Data classification systems
- Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions
- Regular data audits
- Secure data disposal procedures
Legal Compliance and Documentation
- Regulatory Compliance
- Working with some of the best lawyers in Sri Lanka can help ensure your business:
- Compliance Requirements
- Adheres to local and international data protection laws
- Maintains detailed compliance documentation
- Implements required privacy policies
- Follows proper incident reporting procedures
- Conducts regular compliance audits
- Documentation Practices
- Maintain detailed incident logs
- Record all security measures implemented
- Document employee training completion
- Keep audit trails of all security-related activities
- Maintain up-to-date compliance certificates
- Vendor Management
- Vendor Security Assessment
- Detailed security questionnaires
- Regular vendor security audits
- Clear security requirements in contracts
- Incident response coordination plans
- Data handling agreements and requirements
- Ongoing Monitoring
- Regular vendor performance reviews
- Security compliance checks
- Service level agreement monitoring
- Risk assessment updates
- Communication protocols
Crisis Management and Response
- Incident Response Plan
- Comprehensive Response Procedures
- Detailed step-by-step response protocols
- Clear communication channels
- Legal consultation procedures
- Customer notification processes
- Evidence preservation guidelines
- System recovery strategies
- Team Structure
- Incident response team composition
- Clear roles and responsibilities
- Emergency contact information
- External resource coordination
- Escalation procedures
- Regular Testing and Updates
- Testing Protocols
- Monthly security drills
- Quarterly backup system tests
- Annual full-scale incident response exercises
- Regular vulnerability assessments
- Penetration testing schedules
Cost-Effective Implementation
- Prioritise Security Investments
- Budget Planning
- Risk-based investment approach
- Critical asset protection prioritisation
- Regular budget reviews and adjustments
- ROI assessment of security measures
- Cost-benefit analysis of security tools
- Resource Allocation
- Staff training investments
- Technology infrastructure upgrades
- Security tool acquisitions
- External consultancy services
- Emergency response funds
Future-Proofing Your Business
- Emerging Threats and Technologies
- Stay Informed About:
- Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity
- Blockchain security applications
- Internet of Things (IoT) security
- Cloud security developments
- Zero-trust architecture
- Quantum computing threats
- 5G security implications
- Adaptation Strategies
- Regular technology assessments
- Innovation integration plans
- Security roadmap development
- Skills development programs
- Partnership opportunities
Cybercrime is an evolving threat that requires constant vigilance and adaptation. By implementing these comprehensive security measures, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of becoming cybercrime victims. Remember that cybersecurity is not a one-time implementation but a continuous process of improvement and adaptation.
The key to success lies in taking a proactive approach to security, maintaining strong partnerships with legal and security professionals, and fostering a security-conscious culture within your organisation. By staying informed about the latest threats and regularly updating your security measures, your business can maintain robust protection against cyber threats while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Investment in cybersecurity should be viewed as a fundamental business requirement rather than an optional expense. In today's digital landscape, the question is not if a cyber-attack will occur, but when. Therefore, preparing your business with robust security measures is essential for long-term survival and success in the digital age.
Organisations must remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility that requires commitment from all levels of the organisation, from the board room to the front line. By creating a culture of security awareness and implementing comprehensive protection measures, businesses can better position themselves to face the challenges of an increasingly complex cyber threat landscape.