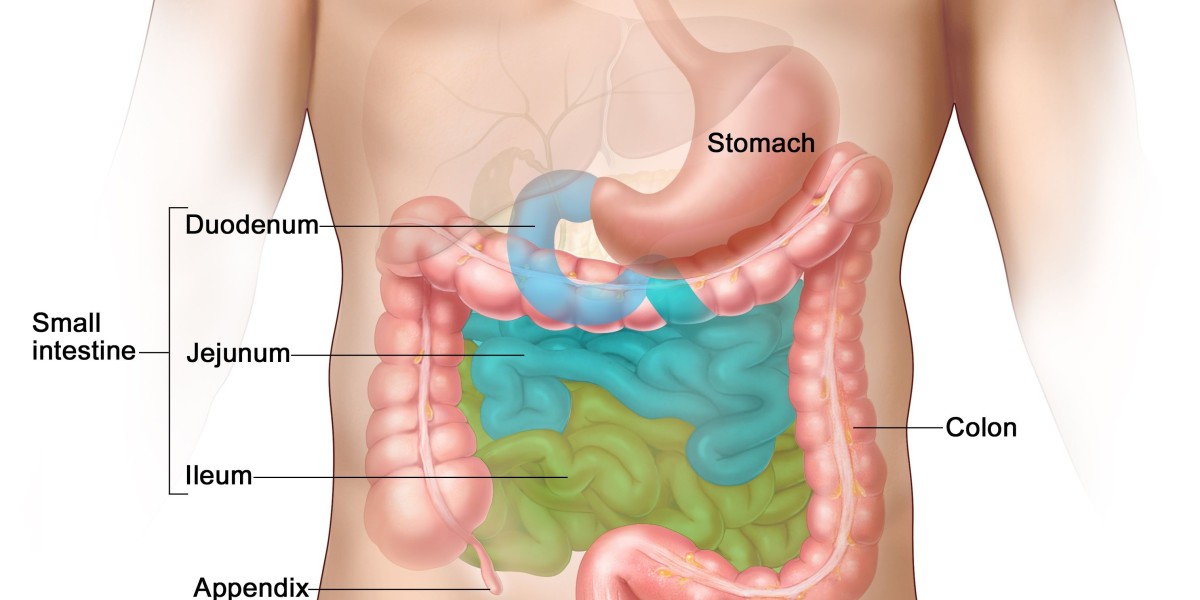
Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Analysis Overview
The gastric neuroendocrine tumor (gNET) drug pipeline is a growing area of interest, with increasing focus on developing targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and novel drug candidates that could offer significant advancements in treating this rare cancer. GNETs are a subtype of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), and while NETs have seen progress in terms of new treatments, gastric-specific drugs and therapies remain under development.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/gastric-neuroendocrine-tumors-drug-pipeline-insight/requestsample
Key Features of the Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumor Pipeline
Targeted Therapies: These therapies are designed to attack specific targets on cancer cells. They have the potential to treat gNETs with greater precision and fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy: Several immunotherapeutic approaches, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, are being evaluated to see if they can stimulate the immune system to fight gastric neuroendocrine tumors more effectively.
Combination Therapies: Research is focusing on the combination of existing therapies with newer, targeted agents to enhance therapeutic effectiveness in gNET patients.
Biomarker Identification: Identifying biomarkers specific to gastric neuroendocrine tumors is crucial for developing personalised treatment strategies. This approach allows for more tailored therapies and a better understanding of patient responses.
Orphan Drug Status: Given the rarity of gastric neuroendocrine tumors, many drugs in the pipeline are seeking orphan drug status, which provides financial incentives for the development of therapies for rare diseases.
The overall aim is to expand the range of effective treatment options for gNET patients, especially those with advanced disease or those who do not respond well to traditional therapies.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/gastric-neuroendocrine-tumors-drug-pipeline-insight
Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Dynamics
The dynamics of the gastric neuroendocrine tumor drug pipeline are shaped by various factors, including market demand, scientific advancements, regulatory landscapes, and emerging treatment strategies.
1. Market Demand and Unmet Needs
The rarity of gastric neuroendocrine tumors means there is a relatively small but crucial patient population in need of new and improved therapies. Current treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and somatostatin analogs, may not always provide long-term relief or effectively control the disease in its advanced stages. The need for more effective treatments, especially for metastatic and inoperable tumors, drives the demand for innovative drugs that can target the disease at a molecular level.
2. Scientific Advancements in Targeted Therapy
One of the key dynamics of the pipeline is the focus on targeted therapy. These therapies are designed to block specific molecules involved in tumor growth, allowing for more precise and less toxic treatments. The success of targeted therapies in other forms of cancer, such as lung cancer and breast cancer, has spurred interest in their potential for gastric neuroendocrine tumors. Drugs like Lenvatinib and Everolimus, which target specific pathways involved in tumor progression, are being tested in clinical trials for gNETs.
3. Advances in Immunotherapy
Immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, are showing promise for many types of cancer, and research is increasingly focusing on their potential in neuroendocrine cancers. These therapies work by boosting the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. Drugs such as nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda), which have shown success in other cancers, are currently under investigation in gNET trials.
4. Regulatory Landscape and Orphan Drug Status
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA are actively supporting the development of treatments for rare cancers, including gNETs, through orphan drug status. This status provides benefits such as market exclusivity, tax credits, and faster approval processes for treatments targeting rare diseases, which in turn encourages investment and innovation in the field.
5. Combination Therapies
Combination therapies are becoming a promising strategy for treating gastric neuroendocrine tumors. These combinations may include targeted agents, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy to enhance the overall effectiveness and extend survival rates for patients. Several ongoing trials are exploring the efficacy of combining different treatment modalities to improve patient outcomes.
External Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Trends
Several external trends are shaping the development of gastric neuroendocrine tumor treatments, including technological advances, changing healthcare policies, and shifts in clinical focus.
1. Technological Advances in Precision Medicine
The rise of genomic sequencing and biomarker discovery is enabling a more personalised approach to cancer treatment. By identifying specific genetic mutations and biomarkers in gNET patients, therapies can be tailored to the individual, potentially improving treatment outcomes. The use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies is allowing for the identification of molecular targets that could guide the development of more effective drugs.
2. Increased Focus on Rare Cancers
As rare cancers like gNETs receive more attention from both the scientific community and pharmaceutical companies, we are seeing an increase in research funding, clinical trials, and drug development in the area. Organizations such as the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) are helping to support and promote research into rare cancers, including gastric neuroendocrine tumors.
3. Patient Advocacy and Awareness
The growing efforts by patient advocacy groups to raise awareness of gastric neuroendocrine tumors are helping to bring attention to the unmet needs of gNET patients. These groups are not only pushing for more research but also working to improve patient access to the latest treatments.
4. Global Access to Treatment
As drug development progresses, ensuring global access to these therapies is becoming increasingly important. While targeted therapies and immunotherapies show great promise in clinical trials, ensuring that these treatments reach underserved populations is a key external trend. Global health initiatives and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and government bodies will be essential to improving treatment accessibility.
Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Analysis Segmentation
The gastric neuroendocrine tumor pipeline can be segmented by several factors, including drug type, development stage, and therapeutic approach.
1. By Drug Type
- Targeted Therapies: These drugs target specific molecules or pathways involved in tumor growth.
- Immunotherapies: Includes immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and therapeutic vaccines.
- Chemotherapy: Traditional treatments that work by targeting rapidly dividing cells.
- Hormonal Therapies: Includes drugs that influence hormone levels to control tumor growth.
2. By Development Stage
- Preclinical Stage: Drugs that are still undergoing laboratory research or early animal testing.
- Phase I: Initial human testing to evaluate safety and dosage.
- Phase II & III: Further trials to assess the effectiveness of drugs and monitor for side effects.
- Marketed Drugs: Drugs that have completed clinical trials and received approval for use.
3. By Therapeutic Approach
- Monotherapy: Single-drug treatment options.
- Combination Therapy: Treatment strategies that combine two or more drugs, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy.
Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Growth
The growth of the gastric neuroendocrine tumor drug pipeline is driven by multiple factors, including:
1. Research and Development Investment
Continued investment in research is accelerating the development of novel therapies for gNETs. As pharmaceutical companies focus more on rare cancers, new therapies are expected to emerge, improving treatment options for gNET patients.
2. Technological Advancements in Drug Development
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and machine learning in drug discovery is revolutionising the way new treatments are identified and developed for gastric neuroendocrine tumors. These technologies can help speed up the identification of potential drug candidates and predict their success in clinical trials.
3. Regulatory Support
The continued support from regulatory agencies, including fast-tracking and accelerated approvals, is encouraging the development of effective treatments for gNETs.
Recent Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline Market
The recent market trends for gastric neuroendocrine tumors drug pipeline indicate significant growth, with an increasing number of therapies entering clinical trials. The combination of innovative therapies, personalised medicine, and global collaboration is likely to create a robust market for gNET treatments over the next few years.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted many areas of healthcare, including clinical trials and drug development. Many studies, including those related to gastric neuroendocrine tumors, faced delays due to restrictions on patient recruitment, lockdowns, and reallocation of healthcare resources. However, the pandemic has also highlighted the importance of developing innovative, remote monitoring strategies and improving patient care, which may have long-term benefits for gNET treatment development.
Key Players in the Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Drug Pipeline
Several pharmaceutical companies are leading the way in the development of gastric neuroendocrine tumor treatments:
- Ipsen – A key player in the development of targeted therapies and somatostatin analogs for neuroendocrine tumors.
- Camurus AB – Focused on developing long-acting therapies for the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors.
- TaiRx, Inc. – Developing novel biologics and immunotherapies aimed at improving treatment outcomes for gNET patients.
FAQ
1. What are gastric neuroendocrine tumors (gNETs)?
Gastric neuroendocrine tumors (gNETs) are rare cancers that form in the gastrointestinal tract, primarily in the stomach. They account for around 8% of all neuroendocrine tumors.
2. What are the treatment options for gNETs?
Current treatments include surgical resection, chemotherapy, and somatostatin analogs. New treatments under investigation include targeted therapies and immunotherapy.
3. What is the focus of research in the gNET drug pipeline?
The focus of research is on targeted therapies, combination therapies, and immunotherapies that can offer more effective and precise treatment for gNET patients.
4. Who are the key players in the gNET drug pipeline?
Key players in the gNET pipeline include Ipsen, Camurus AB, and TaiRx, Inc..